Association Between Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Very Preterm Infants: A Bayesian Model-Averaged Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40564720
- PMCID: PMC12191783
- DOI: 10.3390/children12060762
Association Between Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Very Preterm Infants: A Bayesian Model-Averaged Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Prenatal adverse events may influence the development of complications of prematurity, including patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). We conducted a systematic review and Bayesian model-averaged (BMA) meta-analysis of observational studies exploring the association between hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) and the risk of PDA in preterm infants. Methods: PubMed/Medline and Embase databases were searched. We used BMA analysis to calculate Bayes factors (BFs). The BF10 is the ratio of the probability of the data under the alternative hypothesis (H1, presence of association) over the probability of the data under the null hypothesis (H0, absence of association). Results: We included 41 studies (58,004 infants). BMA analysis showed moderate evidence in favour of H0 for the association between HDP and any PDA (BF10 = 0.20) as well as for the association between HDP and hemodynamically significant PDA (BF10 = 0.27). Subgroup analyses based on the subtype of HDP showed that the moderate evidence in favour of H0 was only conclusive (i.e., BF10 < 0.33) for the associations of any PDA with preeclampsia (BF10 = 0.30) and hemodynamically significant PDA with preeclampsia (BF10 = 0.17). Conclusions: The currently available evidence suggests a lack of association between HDP and the risk of developing PDA.
Keywords: Bayesian statistics; meta-analysis; patent ductus arteriosus; preeclampsia; preterm infant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
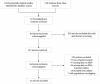
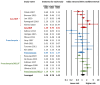
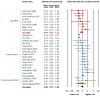
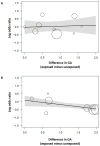
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

