Risk of Bias Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies Using QUADAS 2 by Large Language Models
- PMID: 40564772
- PMCID: PMC12191753
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15121451
Risk of Bias Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies Using QUADAS 2 by Large Language Models
Abstract
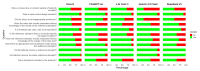
Background/Objectives: Diagnostic accuracy studies are essential for the evaluation of the performance of medical tests. The risk of bias (RoB) for these studies is commonly assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS) tool. This study aimed to assess the capabilities and reasoning accuracy of large language models (LLMs) in evaluating the RoB in diagnostic accuracy studies, using QUADAS 2, compared to human experts. Methods: Four LLMs were used for the AI assessment: ChatGPT 4o model, X.AI Grok 3 model, Gemini 2.0 flash model, and DeepSeek V3 model. Ten recent open-access diagnostic accuracy studies were selected. Each article was independently assessed by human experts and by LLMs using QUADAS 2. Results: Out of 110 signaling questions assessments (11 questions for each of the 10 articles) by the four AI models, and the mean percentage of correct assessments of all the models was 72.95%. The most accurate model was Grok 3, followed by ChatGPT 4o, DeepSeek V3, and Gemini 2.0 Flash, with accuracies ranging from 74.45% to 67.27%. When analyzed by domain, the most accurate responses were for "flow and timing", followed by "index test", and then similarly for "patient selection" and "reference standard". An extensive list of reasoning errors was documented. Conclusions: This study demonstrates that LLMs can achieve a moderate level of accuracy in evaluating the RoB in diagnostic accuracy studies. However, they are not yet a substitute for expert clinical and methodological judgment. LLMs may serve as complementary tools in systematic reviews, with compulsory human supervision.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; diagnostic accuracy; evidence-based medicine; large language models; risk of bias.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Whiting P.F., Rutjes A.W.S., Westwood M.E., Mallett S., Deeks J.J., Reitsma J.B., Leeflang M.M.G., Sterne J.A.C., Bossuyt P.M.M., the QUADAS-2 Group QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011;155:529–536. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- University of Bristol QUADAS. [(accessed on 12 May 2025)]. Available online: https://www.bristol.ac.uk/population-health-sciences/projects/quadas/
-
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Definition, Examples, Types, Applications, Companies, & Facts | Britannica. [(accessed on 12 May 2025)]. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/technology/artificial-intelligence.
-
- What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? | IBM. [(accessed on 12 May 2025)]. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/artificial-intelligence.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

