The Validation of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Software for the Detection and Numbering of Primary Teeth on Panoramic Radiographs
- PMID: 40564810
- PMCID: PMC12192283
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15121489
The Validation of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Software for the Detection and Numbering of Primary Teeth on Panoramic Radiographs
Abstract
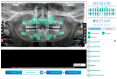
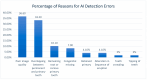
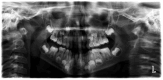
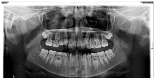
Background: Dental radiographs play a crucial role in diagnosis and treatment planning. With the rise in digital imaging, there is growing interest in leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to support clinical decision-making. AI technologies can enhance diagnostic accuracy by automating tasks like identifying and locating dental structures. The aim of the current study was to assess and validate the accuracy of an AI-powered application in the detection and numbering of primary teeth on panoramic radiographs. Methods: This study examined 598 archived panoramic radiographs of subjects aged 4-14 years old. Images with poor diagnostic quality were excluded. Three experienced clinicians independently assessed each image to establish the ground truth for primary teeth identification. The same radiographs were then evaluated using EM2AI, an AI-based diagnostic software for the automatic detection and numbering of primary teeth. The AI's performance was assessed by comparing its output to the ground truth using sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, accuracy, and the Kappa coefficient. Results: EM2AI demonstrated high overall performance in detecting and numbering primary teeth in mixed dentition, with an accuracy of 0.98, a sensitivity of 0.97, a specificity of 0.99, and a Kappa coefficient of 0.96. Detection accuracy for individual teeth ranged from 0.96 to 0.99. The highest sensitivity (0.99) was observed in detecting upper right canines and primary molars, while the lowest sensitivity (0.79-0.85) occurred in detecting lower incisors and the upper left first molar. Conclusions: The AI module demonstrated high accuracy in the automatic detection of primary teeth presence and numbering in panoramic images, with performance metrics exceeding 90%. With further validation, such systems could support automated dental charting, improve electronic dental records, and aid clinical decision-making.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; panoramic radiography; primary teeth; sensitivity and specificity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence for detecting keratoconus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 15;11(11):CD014911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014911.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37965960 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning approach to direct immunofluorescence pattern recognition in autoimmune bullous diseases.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jul 16;191(2):261-266. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae142. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38581445
-
Diagnostic accuracy of an artificial intelligence-based software in detecting supernumerary and congenitally missing teeth in panoramic radiographs.Eur J Orthod. 2025 Jun 12;47(4):cjaf054. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjaf054. Eur J Orthod. 2025. PMID: 40616472 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of an artificial intelligence-based platform in detecting periapical radiolucencies on cone-beam computed tomography scans of molars.J Dent. 2025 Sep;160:105854. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2025.105854. Epub 2025 May 31. J Dent. 2025. PMID: 40456383
References
-
- Evangelista K., de Freitas Silva B.S., Yamamoto-Silva F.P., Valladares-Neto J., Silva M.A.G., Soares Cevidanes L.H., de Luca Canto G., Massignan C. Accuracy of artificial intelligence for tooth extraction decision-making in orthodontics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022;26:6893–6905. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04742-0. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

