Validation of Axial Juvenile Spondyloarthropathy Criteria in Turkish Juvenile Spondyloarthropathy Patients
- PMID: 40564817
- PMCID: PMC12191953
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15121498
Validation of Axial Juvenile Spondyloarthropathy Criteria in Turkish Juvenile Spondyloarthropathy Patients
Abstract
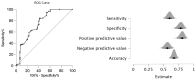
Background: Juvenile spondyloarthritis (JSpA) is a heterogeneous group of diseases. An international consensus group developed the axial juvenile SpA (AxJSpA) classification criteria for this purpose, defining a homogeneous group of patients diagnosed with jSpA and experiencing axial symptoms before the age of 18 years. Aim: To validate this new set of criteria in our pediatric SpA patients. Methods: This study was held in the Hacettepe University Department of Pediatric Rheumatology. Juvenile SpA patients suspected of axial disease diagnosed and followed at the same center between 2005 and 2024 were included. Patients who had other etiologies for axial symptoms, including chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis, mechanical back pain-overuse injuries, amplified pain/growing pains, and SAPHO syndrome (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis) served as the control group. Results: In total, 123 JSpA patients and 74 controls were included in this study. The sensitivity/specificity of the new criteria were 61%/77% with an area under curve value of 0.75 (95% CI: 0.68-0.83) in our cohort. Among different criteria sets, European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) criteria were the most sensitive (sensitivity/specificity 91%/68%), and ASAS peripheral criteria (Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society) were the most specific (sensitivity/specificity 67%/84%) in our cohort when compared to ASAS axial criteria (sensitivity/specificity 74%/65%), ILAR (International League of Associations for Rheumatology) (sensitivity/specificity 85%/81%), and ILAR + SI (sacroiliitis) (sensitivity/specificity 67%/74%) criteria. Conclusions: The area under the curve of the new AxJSpA criteria was similar to that of the original report; however, both sensitivity and specificity were lower in our cohort, possibly due to factors like earlier disease presentation and a lower prevalence of chronic structural changes on MRI.
Keywords: arthritis; axial spondyloarthritis; classification; enthesitis; spondyloarthropathies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the absence of any present or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nordal E., Zak M., Aalto K., Berntson L., Fasth A., Herlin T., Lahdenne P., Nielsen S., Straume B., Rygg M. Ongoing disease activity and changing categories in a long-term nordic cohort study of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:2809–2818. doi: 10.1002/art.30426. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oen K., Duffy C.M., Tse S.M., Ramsey S., Ellsworth J., Chédeville G., Chetaille A.L., Saint-Cyr C., Cabral D.A., Spiegel L.R., et al. Early outcomes and improvement of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis enrolled in a Canadian multicenter inception cohort. Arthritis Care Res. 2010;62:527–536. doi: 10.1002/acr.20044. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weiss P.F., Beukelman T., Schanberg L.E., Kimura Y., Colbert R.A. Enthesitis-related arthritis is associated with higher pain intensity and poorer health status in comparison with other categories of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: The Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance Registry. J. Rheumatol. 2012;39:2341–2351. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.120642. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources