Nature-Inspired Multi-Level Thresholding Integrated with CNN for Accurate COVID-19 and Lung Disease Classification in Chest X-Ray Images
- PMID: 40564821
- PMCID: PMC12191785
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15121500
Nature-Inspired Multi-Level Thresholding Integrated with CNN for Accurate COVID-19 and Lung Disease Classification in Chest X-Ray Images
Abstract
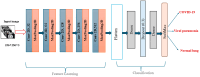
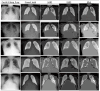
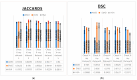
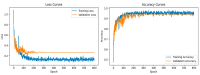
Background/Objectives: Accurate classification of COVID-19 from chest X-rays is critical but remains limited by overlapping features with other lung diseases and the suboptimal performance of current methods. This study addresses the diagnostic gap by introducing a novel hybrid framework for precise segmentation and classification of lung conditions. Methods: The approach combines multi-level thresholding with the advanced metaheuristic optimization algorithms animal migration optimization (AMO), electromagnetism-like optimization (EMO), and the harmony search algorithm (HSA) to enhance image segmentation. A convolutional neural network (CNN) is then employed to classify segmented images into COVID-19, viral pneumonia, or normal categories. Results: The proposed method achieved high diagnostic performance, with 99% accuracy, 99% sensitivity, and 99.5% specificity, confirming its robustness and effectiveness in clinical image classification tasks. Conclusions: This study offers a novel and technically integrated solution for the automated diagnosis of COVID-19 and related lung conditions. The method's high accuracy and computational efficiency demonstrate its potential for real-world deployment in medical diagnostics.
Keywords: COVID-19 diagnosis; animal migration optimization; chest X-ray classification; convolutional neural network; electromagnetism-like optimization; harmony search algorithm; multi-level thresholding.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Advanced glaucoma disease segmentation and classification with grey wolf optimized U -Net++ and capsule networks.Int Ophthalmol. 2025 Jun 27;45(1):266. doi: 10.1007/s10792-025-03602-6. Int Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40576831
-
A deep learning approach to direct immunofluorescence pattern recognition in autoimmune bullous diseases.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jul 16;191(2):261-266. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae142. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38581445
-
Medical image segmentation approach based on hybrid adaptive differential evolution and crayfish optimizer.Comput Biol Med. 2024 Sep;180:109011. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.109011. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39146840
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 16;5(5):CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35575286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global COVID-19 Situation Report—January 2024. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2024. (WHO Technical Report Series).
-
- Karcioglu O., editor. New COVID-19 Variants—Diagnosis and Management in the Post-Pandemic Era: Diagnosis and Management in the Post-Pandemic Era. BoD–Books on Demand; Hamburg, Germany: 2024.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

