A Novel Concept of the "Standard Human" in the Assessment of Individual Total Heart Size: Lessons from Non-Contrast-Enhanced Cardiac CT Examinations
- PMID: 40564823
- PMCID: PMC12192549
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15121502
A Novel Concept of the "Standard Human" in the Assessment of Individual Total Heart Size: Lessons from Non-Contrast-Enhanced Cardiac CT Examinations
Abstract
Background: This single-center retrospective observational study reviewed data from 2305 persons examined for coronary artery calcium (CAC) with non-contrast-enhanced cardiac CT. Other cardiac structures, including chamber volumes, were evaluated besides the CAC scoring. We proposed a novel body size indexing measure that may outperform common indices for quantifying total heart volume (THV). Methods: This index is the sum of height and the difference between height (unitless) and body surface area (unitless), [h+(h-BSA)], and if the (h-BSA) equals "zero", it is a feature of the "standard human". Results: We found that, in subjects with a low cardiovascular (CV) risk, the THV normalized for the novel index was simply a function of BW gain, being the highest in obese. If high-CV-risk features (hypertension, diabetes) were present, the measured THV was larger than expected for BW gain, exceeding values observed in low-CV-risk ones. Differences were found to be sex-independent in all BMI categories. Conclusions: Common BSA correction hides these differences and makes the prognostication of CV risk error-introducing. The indexation we proposed might help distinguish the effects of body weight gain from the ones resulting from the presence of certain cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: coronary artery calcium; standard human; total heart volume.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
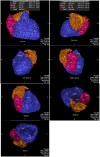
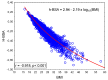
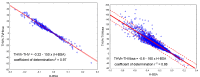
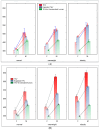
Similar articles
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of computed tomography screening for coronary artery disease: systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Oct;10(39):iii-iv, ix-x, 1-41. doi: 10.3310/hta10390. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17018228
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Lopez-Jimenez F., Almahmeed W., Bays H., Cuevas A., Di Angelantonio E., le Roux C.W., Sattar N., Sun M.C., Wittert G., Pinto F.J., et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Mechanistic insights and management strategies. A joint position paper by the World Heart Federation and World Obesity Federation. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022;29:2218–2237. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwac187. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

