Study of MicroRNA-192 as an Early Biomarker for Diagnosis of Diabetic Nephropathy
- PMID: 40564825
- PMCID: PMC12191681
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15121504
Study of MicroRNA-192 as an Early Biomarker for Diagnosis of Diabetic Nephropathy
Abstract
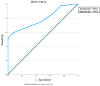
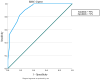
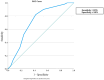
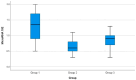
Background/Objectives: Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus. This clinical condition is diagnosed through the detection of microalbuminuria. Molecular biomarkers such as MicroRNA-192 may play a role in the early diagnosis of this condition. This study aims to compare the serum concentrations of MicroRNA-192 in diabetic patients with and without DN and in healthy individuals. Methods: This study was a retrospective case-control study that included three groups. Group I included diabetic patients without DN, Group II included patients with DN, and Group III included healthy control subjects. Blood samples were obtained from each participant and subjected to a full biochemical study including creatinine, albumin, and the detection of MicroRNA-192 by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Results: There were significant differences among the MicroRNA-192 levels in the three groups (p-0.001). There was a significant increase in the MicroRNA-192 level in Group I (1.35 ± 7 0.5) compared with Group II (0.65 ± 7 0.2, p3 = 0.001) and Group III (0.83 ± 7 0.3, p1-0.001). There was a significant reduction in the MicroRNA-192 level in Group II compared with Group III (p2-0.001). Conclusions: This study highlights the potential role of serum miR-192 as a noninvasive biomarker for the early detection of DN in patients with type 2 DM. Our findings demonstrated that serum miR-192 levels were significantly reduced in patients with DN compared with diabetic patients without nephropathy and healthy controls, suggesting the possible protective role of miR-192 in early disease stages.
Keywords: DM type 2; MicroRNA-192; albuminuria; diabetic nephropathy; eGFR.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest for any of the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Shahin D.H.H., Sultana R., Farooq J., Taj T., Khaiser U.F., Alanazi N.S.A., Alshammari M.K., Alshammari M.N., Alsubaie F.H., Asdaq S.M.B., et al. Insights into the uses of traditional plants for diabetes nephropathy: A review. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022;44:2887–2902. doi: 10.3390/cimb44070199. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu C., Sun L., Xiao L., Han Y., Fu X., Xiong X., Xu X., Liu Y., Yang S., Liu F., et al. Insight into the mechanisms involved in the expression and regulation of extracellular matrix proteins in diabetic nephropathy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015;22:2858–2870. doi: 10.2174/0929867322666150625095407. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

