Klebsiella pneumoniae Invasive Liver Abscess Syndrome (Klas/Ilas)-Experience of a Single Center and Up-to-Date Review of the Literature
- PMID: 40564854
- PMCID: PMC12191779
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15121533
Klebsiella pneumoniae Invasive Liver Abscess Syndrome (Klas/Ilas)-Experience of a Single Center and Up-to-Date Review of the Literature
Abstract
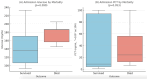
Background: Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess (KLAS) is a potentially life-threatening condition with variable outcomes. Identifying risk factors for mortality is crucial for improving patient management. We aimed to analyze factors associated with in-hospital mortality in a cohort of patients with KLAS and review current diagnostic and treatment challenges. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed clinical, laboratory, microbiological, and treatment data from 20 patients admitted with KLAS. Patients were divided into survivor (n = 15) and non-survivor (n = 5) groups. Univariate analyses were performed using appropriate statistical tests to compare groups and identify mortality-related factors. Results: The overall in-hospital mortality rate was 25.0% (5/20). Factors significantly associated with mortality included undergoing laparotomy drainage (60.0% vs. 6.7%, p = 0.018) and developing in-hospital complications (80.0% vs. 6.7%, p = 0.002). Laparoscopic drainage was significantly associated with survival (93.3% vs. 40.0%, p = 0.026). Trends toward increased mortality were observed with diabetes mellitus and higher glucose levels at admission. Despite p-values < 0.05 from prior Fisher's exact test, and the fact that ESBL positivity (OR = 22, 95% CI 0.86-571.32) and septic shock at admission (OR = 16.08, 95% CI 0.75-343.64) showed a very high point estimate for risk of mortality, the association was not statistically significant in our study. Conclusions: Mortality in this KLAS cohort was considerable. The necessity for open drainage and the development of in-hospital complications emerged as significant predictors of death, while other independent risk factor such as diabetes mellitus, high blood glucose levels at admission, septic shock at admission, and ESBL-positive strains indicated a trend towards unfavorable outcomes. These findings underscore the importance of aggressive sepsis management and addressing antimicrobial resistance. Conflicting results regarding the statistical significance of independent risk factors due to a limited sample size highlight the need for larger studies to confirm these findings.
Keywords: KLAS; Klebsiella liver abscess; abdominal sepsis; antimicrobial resistance; invasive liver abscess.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive ventilation for the management of acute hypercapnic respiratory failure due to exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 13;7(7):CD004104. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004104.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28702957 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Maternal and neonatal outcomes of elective induction of labor.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009 Mar;(176):1-257. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009. PMID: 19408970 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Cardenas-Alvarez J., Balayla G., Triana A., Diaz Lankenau R., Franco-Paredes C., Henao-Martinez A.F., Motoa G. Clinical Spectrum and Outcomes of Cryptogenic Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscess in the Americas: A Scoping Review. Pathogens. 2023;12:661. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12050661. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources