Therapeutic Efficacy of Silymarin, Vitamin E, and Essential Phospholipid Combination Therapy on Hepatic Steatosis, Fibrosis, and Metabolic Parameters in MASLD Patients: A Prospective Clinical Study
- PMID: 40564891
- PMCID: PMC12192674
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125427
Therapeutic Efficacy of Silymarin, Vitamin E, and Essential Phospholipid Combination Therapy on Hepatic Steatosis, Fibrosis, and Metabolic Parameters in MASLD Patients: A Prospective Clinical Study
Abstract
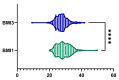
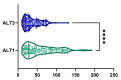
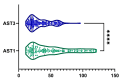
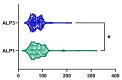
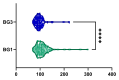
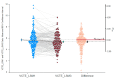
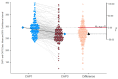
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is the most prevalent chronic liver disease globally, and current estimates indicate an increase in incidence and prevalence in the general population. The design of the prospective study was to evaluate the response of patients with MASLD to an original formula consisting of silymarin, vitamin E, and essential phospholipids. In total, 200 patients were initially enrolled in the study and a total of 190 who participated in all four visits were included in our analysis. During the visits, liver function tests, lipid profiles, blood glucose level, fibrosis, and steatosis values and grades were assessed. From baseline, visit 0, to month 6th, visit III, a statistically significant difference (p-value < 0.0001) was observed in the reduction in ALT, AST, GGT, ALP, TG, total cholesterol, and blood glucose levels. There was a significant decrease in the fibrosis value from the first visit to the last visit (p = 0.002). Even though administered separately, silymarin, essential phospholipids, and vitamin E have established their efficacy in MASLD, this study demonstrates that their combination produces an indubitable effect on liver steatosis, even in a short cure of 6 months, and it can be proposed due to it having no adverse effects on patients with MASLD.
Keywords: MASLD; VCTE; silymarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sylimarin Versus Essential Phospholipids in Metabolic Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) - A Prospective Comparative Randomized Trial.Maedica (Bucur). 2024 Mar;19(1):9-16. doi: 10.26574/maedica.2024.19.1.9. Maedica (Bucur). 2024. PMID: 38736928 Free PMC article.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the health and economic impact of pharmacologic therapies for MASLD in the United States.J Hepatol. 2025 Jul;83(1):21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2025.01.009. Epub 2025 Jan 18. J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39832655
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Tacke F., Horn P., Wai-Sun Wong V., Ratziu V., Bugianesi E., Francque S., Zelber-Sagi S., Valenti L., Roden M., Schick F., et al. EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) J. Hepatol. 2024;81:492–542. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.04.031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Le P., Tatar M., Dasarathy S., Alkhouri N., Herman W.H., Taksler G.B., Deshpande A., Ye W., Adekunle O.A., McCullough A., et al. Estimated Burden of Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in US Adults, 2020 to 2050. JAMA Netw. Open. 2025;8:e2454707. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.54707. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ajmera V., Kim B.K., Yang K., Majzoub A.M., Nayfeh T., Tamaki N., Izumi N., Nakajima A., Idilman R., Gumussoy M., et al. Liver Stiffness on Magnetic Resonance Elastography and the MEFIB Index and Liver-Related Outcomes in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Individual Participants. Gastroenterology. 2022;163:1079–1089.e1075. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.06.073. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

