Inosine, AMP, and Vidarabine: Network Pharmacology and LC-MS Reveal Key Bioactive Compounds in Periplaneta americana for Ulcerative Colitis Management
- PMID: 40564909
- PMCID: PMC12192714
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125446
Inosine, AMP, and Vidarabine: Network Pharmacology and LC-MS Reveal Key Bioactive Compounds in Periplaneta americana for Ulcerative Colitis Management
Abstract
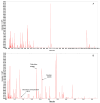
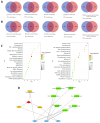
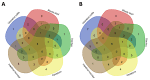
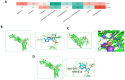
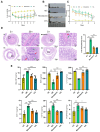
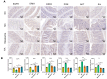
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease with unmet therapeutic needs. This study investigates the therapeutic potential of Periplaneta americana L. extract (PAE) and its molecular mechanisms, integrating network pharmacology and experimental validation. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry identified 1355 compounds in PAE. Network pharmacology analysis revealed that inosine, vidarabine, and adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP) were core components and the core components synergistically regulated key targets and acted on inflammation-related pathways, thereby establishing a multi-target anti-inflammatory regulatory network. In vivo experiments demonstrated that these compounds significantly alleviated colitis symptoms in dextran sulfate sodium-induced mice, as evidenced by reduced disease activity index scores, preserved colonic mucosal architecture, and decreased inflammatory infiltration. Mechanistically, core compounds down-regulated granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)/NOS2, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), and transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), while they up-regulated interleukin-10 (IL-10) and epidermal growth factor (EGF). Additionally, they activated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mediated pathways. Molecular docking analysis revealed that adenosine analogs preferentially bound to A1/A2a receptors, triggering signaling cascades essential for epithelial repair and inflammation resolution. This study established the multi-component, multi-pathway mechanism of PAE in UC, highlighting its dual role in suppressing inflammation and promoting mucosal healing. By bridging traditional herbal use with modern molecular insights, these findings provided a translational foundation for developing PAE-based therapies for UC.
Keywords: Periplaneta americana; adenosine analogs; inflammation; mucosal repair; network pharmacology; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82405020/National Natural Science Fund of China
- 82060780/National Natural Science Fund of China
- 82074580/National Natural Science Fund of China
- 202305AC160034/Yunnan Province Young and Middle aged Academic and Technical Leaders Reserve Talent Pro-ject
- 2025J0819/Yunnan Provincial Education Department Scientific Research Fund
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

