Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Applications: A Review
- PMID: 40564917
- PMCID: PMC12193145
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125454
Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Applications: A Review
Abstract
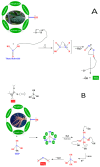
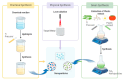
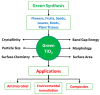
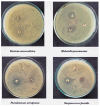
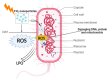
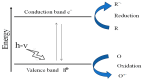
Nanotechnology is an emerging field in science that exhibits significant promise in the synthesis of nanomaterials for diverse applications. Traditionally, these nanomaterials were manufactured using hazardous and labor-intensive physical and chemical processes. Nevertheless, in recent years, researchers have developed safer, more scalable, and environmentally friendly methods for green synthesis. The problem addressed in this study is the need for an environmentally friendly and efficient synthesis process for titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) with enhanced properties. The aim of this work is to describe the synthesis of TiO2 NPs with various plant extracts using a green approach and to evaluate the physicochemical characteristics and potential applications of the resulting nanoparticles. This study focuses on understanding how the integration of plant extracts influences the properties of TiO2 NPs, particularly in terms of their structural, optical, and functional characteristics. The novelty lies in the use of plant extracts as bio-reductants and capping agents, which not only provides a safer and more sustainable synthesis method but also enhances the functional properties of TiO2 NPs. This green synthesis approach reduces the use of harmful chemicals, making the process more environmentally friendly and economically viable, with potential applications in photocatalysis, antibacterial, and antioxidant activities. The TiO2 NPs possess diverse functionalities, including photocatalysis, antibacterial properties, and antioxidant properties. The initial precursor, such as a metal salt, undergoes transformation into the desired nanoparticles through the actions of plants exactly. Bio-reduction and capping processes are carried out by secondary metabolites found in bacteria and plants. The results demonstrated that the plant extract-mediated TiO2 NPs exhibited enhanced photocatalytic activity, superior antibacterial effects, and higher antioxidant potential compared to chemically synthesized TiO2 NPs. This highlights the potential of green synthesis methods in producing nanomaterials with improved functional properties for a wide range of applications.
Keywords: eco-friendly remediation; green chemistry; pollutant degradation; sustainable environmental solutions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phytogenic nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and their roles in physiology and biochemistry of plants.Biometals. 2024 Feb;37(1):23-70. doi: 10.1007/s10534-023-00542-5. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Biometals. 2024. PMID: 37914858 Review.
-
Green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using seeds extract of Cichorium intybus and their comparative analysis with commercially available ointment for wound healing activity.J Mol Histol. 2025 Apr 26;56(3):145. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10426-2. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40285943
-
Green Synthesis and Characterization of Ag Nanoparticles Using Carissa spinarum L. Leaf Extract: Evaluation for Their Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities.Microsc Res Tech. 2025 Aug;88(8):2285-2296. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24817. Epub 2025 Mar 23. Microsc Res Tech. 2025. PMID: 40123114
-
Eco-friendly synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Siirt pistachio thin shell extract: promising applications in photocatalysis and antibacterial solutions.Int J Phytoremediation. 2025 Jul 9:1-13. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2025.2530018. Online ahead of print. Int J Phytoremediation. 2025. PMID: 40635233
-
A Review on Biomedical Applications of Plant Extract-Mediated Metallic Ag, Au, and ZnO Nanoparticles and Future Prospects for Their Combination with Graphitic Carbon Nitride.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 29;18(6):820. doi: 10.3390/ph18060820. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573216 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Visible-Light-Driven Degradation of Biological Contaminants on the Surface of Textile Fabric Modified with TiO2-N Photocatalyst.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 5;26(15):7550. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157550. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xue J., Liu J., Liu Y., Li H., Wang Y., Sun D., Wang W., Huang L., Tang J. Recent advances in synthetic methods and applications of Ag2S-based heterostructure photocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2019;7:3988–4003. doi: 10.1039/C9TC00008A. - DOI
-
- Priyadharsini P., Sundar R.P., Grace P.K., Naveen S., Sanjay K.S., Gnanaprakash D., Arun J., Pugazhendhi A. Nanohybrid photocatalysts in dye (Colorants) wastewater treatment: Recent trends in simultaneous dye degradation, hydrogen production, storage and transport feasibility. J. Clean. Prod. 2023;426:139180. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.139180. - DOI
-
- Bak T., Nowotny J., Rekas M., Sorrell C.C. Photo-electrochemical hydrogen generation from water using solar energy. Materials-related aspects. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2002;27:991–1022. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3199(02)00022-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

