Homocysteinylation of Fibrinogen: A Post-Translational Link to Thrombosis
- PMID: 40564934
- PMCID: PMC12193665
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125471
Homocysteinylation of Fibrinogen: A Post-Translational Link to Thrombosis
Abstract
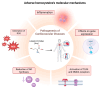
Homocysteinylation, a post-translational modification involving the covalent attachment of homocysteine to proteins, has emerged as a critical mechanism linking hyperhomocysteinemia to thrombotic disease. This review focuses on the homocysteinylation of fibrinogen, a key coagulation factor, and its impact on clot structure and function. Evidence indicates that elevated homocysteine levels can induce significant changes in fibrin architecture, promoting the formation of dense, rigid clots with reduced permeability and impaired fibrinolytic susceptibility, thus fostering a prothrombotic environment. However, inconsistencies in reported effects on fiber diameter and polymerization kinetics highlight the need for standardized experimental protocols. Advances in proteomics and high-resolution imaging are expected to clarify the molecular underpinnings of these modifications. Moreover, homocysteinylation intersects with oxidative stress and may serve as a mechanistic bridge between metabolic and vascular dysfunction. Understanding its role not only enhances insight into thrombosis but also opens avenues for biomarker discovery and targeted therapies in cardiovascular and potentially neurological disorders.
Keywords: fibrinogen; homocysteine; homocysteinylation; oxidation; oxidative stress; thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical