Omega-3 Fatty Acids Mitigate Long-Lasting Disruption of the Endocannabinoid System in the Adult Mouse Hippocampus Following Adolescent Binge Drinking
- PMID: 40564971
- PMCID: PMC12192632
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125507
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Mitigate Long-Lasting Disruption of the Endocannabinoid System in the Adult Mouse Hippocampus Following Adolescent Binge Drinking
Abstract
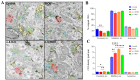
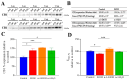
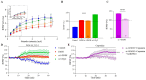
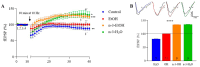
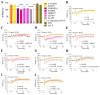
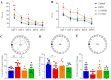
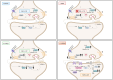
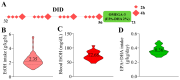
Adolescent binge drinking has lasting behavioral consequences by disrupting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and depleting brain omega-3. The natural accumulation of omega-3 fatty acids in cell membranes is crucial for maintaining the membrane structure, supporting interactions with the ECS, and restoring synaptic plasticity and cognition impaired by prenatal ethanol (EtOH) exposure. However, it remains unclear whether omega-3 supplementation can mitigate the long-term effects on the ECS, endocannabinoid-dependent synaptic plasticity, and cognition following adolescent binge drinking. Here, we demonstrated that omega-3 supplementation during EtOH withdrawal increases CB1 receptors in hippocampal presynaptic terminals of male mice, along with the recovery of receptor-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding to Gαi/o proteins. These changes are associated with long-term potentiation (LTP) at excitatory medial perforant path (MPP) synapses in the dentate gyrus (DG), which depends on anandamide (AEA), transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. Finally, omega-3 intake following binge drinking reduced the time and number of errors required to locate the escape box in the Barnes maze test. Collectively, these findings suggest that omega-3 supplementation restores Barnes maze performance to levels comparable to those of control mice after adolescent binge drinking. This recovery is likely mediated by modulation of the hippocampal ECS, enhancing endocannabinoid-dependent excitatory synaptic plasticity.
Keywords: CB1 receptor; alcohol; hippocampus; memory; polyunsaturated fatty acids; synaptic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peñasco S., Rico-Barrio I., Puente N., Fontaine C.J., Ramos A., Reguero L., Gerrikagoitia I., Rodríguez de Fonseca F., Suárez J., Barrondo S., et al. Intermittent ethanol exposure during adolescence impairs cannabinoid type 1 receptor-dependent long-term depression and recognition memory in adult mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020;45:309–318. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0530-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

