Cherry Juice Improves Memory and Anxiety by Modulating Cell Number in the Hippocampus of Male Rat Pups Infected with Lipopolysaccharides During Gestation and Gestation-Lactation
- PMID: 40565105
- PMCID: PMC12193375
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125642
Cherry Juice Improves Memory and Anxiety by Modulating Cell Number in the Hippocampus of Male Rat Pups Infected with Lipopolysaccharides During Gestation and Gestation-Lactation
Abstract
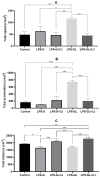
Exposure to lipopolysaccharides (LPS) during pregnancy have been linked to alterations in the offspring's central nervous system. Cherries are a source of anthocyanins, which possess neuroprotective properties. The study aimed to evaluate the neuroprotective effects of cherry juice (CJ) on memory and hippocampal cell counts in offspring exposed to LPS during gestation and the gestation-lactation periods. At postnatal day 90, rat pups were divided into five groups: Control (saline solution), LPS-G (LPS during gestation), LPS-G+CJ (LPS during gestation+CJ), LPS-GL (LPS during gestation-lactation), and LPS-GL+CJ (LPS during gestation-lactation+CJ). A battery of behavioral tests was conducted to assess short- and long-term memory and anxiety-like behavior. Histological analysis was performed on hippocampal regions. Leukocyte levels were measured as markers of systemic inflammation. Results showed that pups in the LPS-G and LPS-GL groups exhibited impaired memory, increased anxiety-like behavior, elevated leukocyte levels, and reduced cell counts in the dentate gyrus and CA1 regions, as well as in CA2 (LPS-G) and CA3 (LPS-GL). Cherry juice administration in the LPS-G+CJ and LPS-GL+CJ groups improved memory performance, normalized leukocyte levels, and restored hippocampal cell counts. These findings suggest that cherry juice exerts neuroprotective effects against LPS-induced neuroinflammation during gestation and the gestation-lactation periods.
Keywords: anxiogenic; cherry juice; leukocyte; locomotor; neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Maternal ingestion of cannabidiol (CBD) in mice leads to sex-dependent changes in memory, anxiety, and metabolism in the adult offspring, and causes a decrease in survival to weaning age.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2025 Feb;247:173902. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2024.173902. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2025. PMID: 39481653
-
Inosine Treatment Attenuates White Matter Injury in Neonatal Rats Exposed to Maternal Inflammation.Neurochem Res. 2025 May 30;50(3):176. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04429-4. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40445478
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
-
Synergistic impact of early-life stress and prenatal immune activation on spatial memory and oxidative metabolism in rat cortico-limbic networks.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2025 May;219:108060. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2025.108060. Epub 2025 May 2. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2025. PMID: 40318801
References
-
- Leclercq S.O., Branger M., Smith D.G.E., Germon P. Lipopolysaccharide core type diversity in the Escherichia coli species in association with phylogeny, virulence gene repertoire and distribution of type vi secretion systems. Microb. Genom. 2021;7:000652. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000652. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

