The Development of a Sensitive and Selective Method for the Quantitative Detection of Ricin via ICP-MS Combined with Metal Element Chelated Tag and Modified Nanoparticles
- PMID: 40565106
- PMCID: PMC12192896
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125641
The Development of a Sensitive and Selective Method for the Quantitative Detection of Ricin via ICP-MS Combined with Metal Element Chelated Tag and Modified Nanoparticles
Abstract
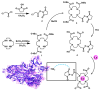
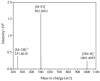
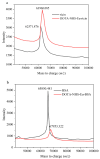
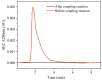
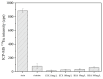
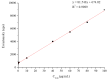
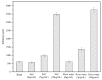
As a type II ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP-II) toxin, Ricin has garnered widespread recognition due to its inherent qualities as an easily prepared and highly stable substance, posing serious implications as a potential chemical and biological terrorist threat. For the detection of ricin, traditional immunoassay technologies, including methods like peptide cleavage combined with liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) or the more commonly used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), have offered reliable results. However, these techniques are unfortunately limited by the requirement of a complex sample pretreatment process, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. In an effort to overcome these limitations, a highly sensitive and selective method was introduced via metal element labeling combined with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) in this research. The method centered on designing and synthesizing a europium-labeled compound (DOTA-NHS-Eu) that specifically targets the amino groups (-NH2) on ricin. The compound, coupled with the application of specific magnetic beads, achieved the specific enrichment and subsequent quantitative detection of ricin by ICP-MS, which is based on the amount of europium element present. The established method demonstrated high specificity for ricin recognition, with a signal response to bovine serum protein that was found to be less than 10% of that for ricin. Furthermore, the calibration curve created for the method (y = 81.543x + 674.02 (R2 > 0.99)) for quantifying ricin in a concentration range of 1.0-100 μg/mL demonstrated good linearity. The method was further evidenced by the limit of detection and quantitation results of 0.1 and 1.89 μg/mL, respectively. Collectively, these findings suggested that the research has offered a highly sensitive and selective method for ricin detection, which was not only easy to operate but also provided efficient results. The scheme showed great potential for the verification of chemical weapons and the destruction of toxic chemicals, therefore representing a significant advancement in the field of biomolecular detection and analysis.
Keywords: inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry; metal element label; quantitative detection; ricin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
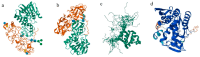

Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
References
-
- Huang S.Z., Qin Z.H. Research progress of biotoxins. J. Toxicol. 2006;20:257–258.
-
- Chen H.X. Research progress of medical application of biotoxins. Biotechnology. 2006;16:84–86. (In Chinese with English abstract)
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

