Studies on the Protective Effect of Silybin Against Low-Dose Radiation-Induced Damage to the Immune System
- PMID: 40565119
- PMCID: PMC12193130
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125656
Studies on the Protective Effect of Silybin Against Low-Dose Radiation-Induced Damage to the Immune System
Abstract
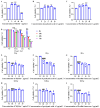
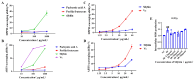
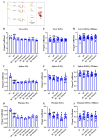
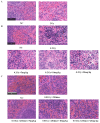
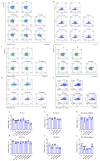
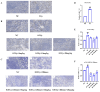
With growing public concern about the health effects of low-dose radiation, numerous studies have demonstrated that low-dose radiation can cause damage to the immune system, making intervention measures essential. This study investigated the protective effects of silybin against low-dose radiation-induced immune system damage and its underlying mechanisms at both the cellular and animal levels. At the cellular level, CCK-8 assays, ROS measurements, and RT-qPCR analysis revealed that silybin alleviated the reduction in RAW264.7 cell proliferation, intracellular ROS levels, and inflammatory cytokine expression following low-dose radiation exposure. At the animal level, comparative analyses of post-irradiation body weight, peripheral blood cell counts, immune organ coefficients, spleen HE/IHC staining, and spleen immune cell numbers demonstrated that silybin mitigated the radiation-induced decrease in body weight, reduction in peripheral blood leukocyte counts, inflammatory cell infiltration in the spleen, decline in spleen immune cell numbers, and increase in cGAS protein-positive cells. These findings indicate that silybin exerts protective effects against low-dose radiation-induced immune system damage, potentially by regulating the cGAS signaling pathway to reduce radiation-induced cellular injury, thereby enhancing its radioprotective properties.
Keywords: immune damage; low-dose radiation; protection; silybin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prevention from radiation damage by natural products.Phytomedicine. 2018 Aug 1;47:192-200. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30166104
-
Interventions to prevent occupational noise-induced hearing loss.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 7;7(7):CD006396. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006396.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28685503 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Rutin Attenuates Oxidative Stress Responses and Hepatocyte Metabolomics in β-Hydroxybutyric Acid-Induced Hepatocyte Injury in Calves.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 19;26(12):5878. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125878. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565341 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic role of TLR2-mediated signaling in the protection of psoralidin against sepsis-induced acute lung injury.Phytomedicine. 2025 Aug;144:156443. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156443. Epub 2025 Feb 1. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40516289
References
-
- Lustig A., Shterev I., Geyer S., Shi A., Hu Y., Morishita Y., Nagamura H., Sasaki K., Maki M., Hayashi I. Long term effects of radiation exposure on telomere lengths of leukocytes and its associated biomarkers among atomic-bomb survivors. Oncotarget. 2016;7:38988–38998. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8801. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vykhovanets E.V., Chernyshov V.P., Slukvin I.I., Antipkin Y.G., Vasyuk A., Colos V. Analysis of blood lymphocyte subsets in children living around Chornobyl exposed long-term to low doses of cesium-137 and various doses of iodine-131. Radiat. Res. 2000;153:760–772. doi: 10.1667/0033-7587(2000)153[0760:AOBLSI]2.0.CO;2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

