Update on HDM Allergy: Principal Changes over the Years
- PMID: 40565123
- PMCID: PMC12193404
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125660
Update on HDM Allergy: Principal Changes over the Years
Abstract
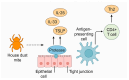
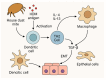
House dust mites (HDMs) are a major source of indoor allergens, significantly contributing to allergic rhinitis, asthma and atopic dermatitis. This review examines the epidemiology, microbiological classification and pathophysiology of HDM allergy, highlighting key allergens such as Der p 1, Der p 2 and Der p 23. Furthermore, we discuss the pivotal role of allergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT), the only disease-modifying treatment for immunoglobulin (Ig)-E disease. Recent studies have identified predictive biomarkers for allergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT) efficacy, including the specific IgE to total IgE (sIgE/tIgE) ratio and regulatory follicular T cell profiles, supporting a more personalized approach to therapy. Additionally, emerging immunotherapy strategies, such as recombinant allergens and peptide-based formulations, aim to improve safety and clinical outcomes. As HDM allergy prevalence rises globally, further research into optimizing diagnostics and treatment strategies remains crucial for enhancing patient care.
Keywords: Der p 1; Dermatophagoides farinae; Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; allergen-specific immunotherapy; allergic rhinitis; asthma; house dust mite allergy; recombinant allergens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Imoto Y., Sakashita M., Tokunaga T., Kanno M., Saito K., Shimizu A., Maegawa A., Fujieda S. Recent prevalence of allergic rhinitis caused by house dust mites among the pediatric population in Fukui, Japan. World Allergy Organ. J. 2024;17:100932. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2024.100932. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

