Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Profile of the Jumonji-C Family Genes in Populus alba × Populus glandulosa Reveal Their Potential Roles in Wood Formation
- PMID: 40565130
- PMCID: PMC12193463
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125666
Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Profile of the Jumonji-C Family Genes in Populus alba × Populus glandulosa Reveal Their Potential Roles in Wood Formation
Abstract
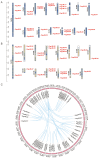
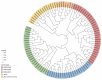
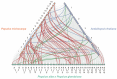
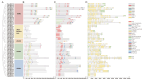
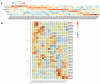
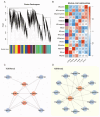
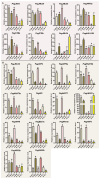
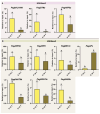
The Jumonji C (JMJ-C) domain-containing gene family regulates epigenetic and developmental processes in plants. We identified 55 JMJ-C genes in Populus alba × Populus glandulosa using HMM and BLASTp analyses. Chromosomal mapping revealed an asymmetric distribution with conserved synteny. Phylogenetic reconstruction revealed that PagJMJ genes segregate into five evolutionarily conserved subfamilies, exhibiting classification patterns identical to those of Arabidopsis thaliana and Populus trichocarpa. Synteny analysis indicated a closer relationship with P. trichocarpa than with A. thaliana. Motif and promoter analyses highlighted subfamily-specific features and diverse cis-elements, particularly light-responsive motifs. Expression profiling revealed tissue-specific patterns, with key genes enriched in roots, vascular tissues, and leaves. Developmental analysis in cambium and xylem identified four expression clusters related to wood formation. Co-expression analysis identified six key PagJMJ genes (PagJMJ6, 29, 34, 39, 53, and 55) strongly associated with wood formation-related transcription factors. ChIP-qPCR analysis revealed that key genes co-expressed with PagJMJ genes were marked by H3K4me3 and H3K9me2 modifications. These findings provide insights into the evolutionary and functional roles of PagJMJ genes in poplar vascular development and wood formation.
Keywords: JMJ-C family; P. alba × P. glandulosa; expression profile; transcription factor; wood formation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Xue Y., Cao X., Chen X., Deng X., Deng X.W., Ding Y., Dong A., Duan C.G., Fang X., Gong L., et al. Epigenetics in the modern era of crop improvements. Sci. China Life Sci. 2025;68:1570–1609. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

