The Anti-Parkinsonian A2A Receptor Antagonist Istradefylline (KW-6002) Attenuates Behavioral Abnormalities, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegeneration in Cerebral Ischemia: An Adenosinergic Signaling Link Between Stroke and Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 40565142
- PMCID: PMC12193193
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125680
The Anti-Parkinsonian A2A Receptor Antagonist Istradefylline (KW-6002) Attenuates Behavioral Abnormalities, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegeneration in Cerebral Ischemia: An Adenosinergic Signaling Link Between Stroke and Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
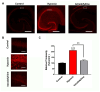
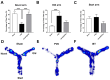
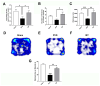
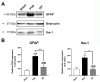
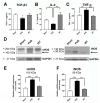
Stroke, the third leading cause of death worldwide, is a major cause of functional disability. Cerebral ischemia causes a rapid elevation of adenosine, the main neuromodulator in the brain. The inhibition of adenosine A2A receptors (A2ARs) has been introduced as a potential target in neurodegenerative disorders involving extracellular adenosine elevation. Istradefylline, a selective A2AR antagonist, has been approved for Parkinson's disease (PD) adjunctive therapy and showed neuroprotective effects in PD and Alzheimer's disease. However, the role of A2ARs in post-stroke neuronal damage and behavioral deficits remains unclear. We recently showed that A2AR antagonism prevented the adenosine-induced post-hypoxia synaptic potentiation of glutamatergic neurotransmission following the hypoxia/reperfusion of hippocampal slices. Here, we investigated the potential neuroprotective effects of istradefylline in male Sprague-Dawley rats subjected to pial vessel disruption (PVD) used to model a small-vessel stroke. Rats were treated with either a vehicle control or istradefylline (3 mg/kg i.p.) following PVD surgery for three days. Istradefylline administration prevented anxiety and depressive-like behaviors caused by PVD stroke. In addition, istradefylline significantly attenuated ischemia-induced cognitive impairment and motor deficits. Moreover, istradefylline markedly reduced hippocampal neurodegeneration, as well as GFAP/Iba-1, TNF-α, nNOS, and iNOS levels after PVD, but prevented the downregulation of anti-inflammatory markers TGF-β1 and IL-4. Together, these results suggest a molecular link between stroke and PD and that the anti-PD drug istradefylline displays translational potential for drug repurposing as a neuroprotective agent for cerebral ischemic damage.
Keywords: adenosine A1 receptor; adenosine A2A receptor; fEPSP; glutamate excitotoxicity; ischemic stroke; istradefylline; stroke model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Benjamin E.J., Virani S.S., Callaway C.W., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Chiuve S.E., Cushman M., Delling F.N., Deo R., de Ferranti S.D., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137:e67–e492. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000558. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Virani S.S., Alonso A., Benjamin E.J., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Delling F.N., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139–e596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

