Pathogenesis and Clinical Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
- PMID: 40565181
- PMCID: PMC12193568
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125717
Pathogenesis and Clinical Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
Abstract
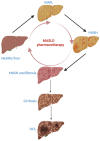
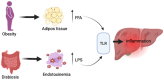
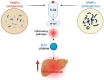
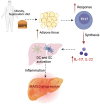
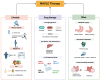
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a chronic progressive liver disease with a substantial impact on global health. Given that MASLD has a complex etiology, it is a multisystemic disease, a multidisciplinary approach is required when treating MASLD. The optimal drug for MASLD should diminish steatosis, fibrosis and inflammation in the liver. Although the pharmaceutical industry is still lagging in developing an approved pharmacologic therapy for MASLD, research has recently intensified, and many molecules that are in the final stages of clinical trials are expected to be approved in the coming few years. The current review updated information related to the MASLD pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapeutic options, how patients are clinically managed nowadays, and what to expect in the near future.
Keywords: MASLD; NAFLD; diagnosis; lifestyle; pathogenesis; therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modeling the health and economic impact of pharmacologic therapies for MASLD in the United States.J Hepatol. 2025 Jul;83(1):21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2025.01.009. Epub 2025 Jan 18. J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39832655
-
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A story of muscle and mass.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 May 28;31(20):105346. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.105346. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40495947 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic-dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease and atrial fibrillation: A review of pathogenesis.World J Cardiol. 2025 Jun 26;17(6):106147. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.106147. World J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40575425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in People With Diabetes: The Need for Screening and Early Intervention. A Consensus Report of the American Diabetes Association.Diabetes Care. 2025 Jul 1;48(7):1057-1082. doi: 10.2337/dci24-0094. Diabetes Care. 2025. PMID: 40434108 Review.
-
Multi-Cohort Exploration of Repetitive Element Transcription and DNA Methylation in Human Steatotic Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 8;26(12):5494. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125494. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lazarus J.V., Mark H.E., Anstee Q.M., Arab J.P., Batterham R.L., Castera L., Cortez-Pinto H., Crespo J., Cusi K., Dirac M.A., et al. Advancing the global public health agenda for NAFLD: A consensus statement. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022;19:60–78. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00523-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American association for the study of liver disease. Latin american association for the study of the liver. European association for the study of the liver A call for unity: The path towards a more precise and patient-centric nomenclature for NAFLD. Hepatology. 2023;78:3–5. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000412. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Riazi K., Azhari H., Charette J.H., Underwood F.E., King J.A., Afshar E.E., Swain M.G., Congly S.E., Kaplan G.G., Shaheen A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022;7:851–861. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

