Skin-Whitening, Antiwrinkle, and Moisturizing Effects of Astilboides tabularis (Hemsl.) Engl. Root Extracts in Cell-Based Assays and Three-Dimensional Artificial Skin Models
- PMID: 40565189
- PMCID: PMC12193470
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125725
Skin-Whitening, Antiwrinkle, and Moisturizing Effects of Astilboides tabularis (Hemsl.) Engl. Root Extracts in Cell-Based Assays and Three-Dimensional Artificial Skin Models
Abstract
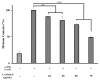
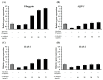
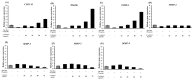
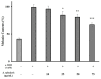
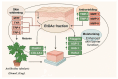
This study investigated the potential cosmetic properties of the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) fraction obtained from the roots of Astilboides tabularis (Hemsl.) Engl., focusing on skin-whitening, antiwrinkle, and moisturizing effects using cell-based assays and three-dimensional (3D) artificial skin models (Neoderm-ED and Neoderm-ME). The EtOAc fraction showed significant dose-dependent inhibitory activity against tyrosinase (TYR) (72.0% inhibition at 50 µg/mL), comparable to that of kojic acid. In α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH)-stimulated Neoderm-ME artificial skin containing melanocytes, the EtOAc fraction reduced melanin synthesis at concentrations of 50 and 75 µg/mL and decreased melanogenesis-related gene expression, including TYR, microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF), tyrosinase-related protein-1 (TRP-1) and TRP-2. In the antiwrinkle assays, the EtOAc fraction effectively inhibited elastase activity (41.5% inhibition at 10 µg/mL), exceeding the efficacy of ursolic acid. In the Neoderm-ED artificial skin model, the EtOAc fraction reversed structural damage induced by particulate matter (PM10), restoring epidermal thickness and dermal density. This improvement was supported by the increased expression of skin barrier and antiwrinkle genes, including filaggrin, hyaluronic acid synthase-1 (HAS-1), HAS-2, aquaporin-3 (AQP-3), collagen type I alpha 1 chain (COL1A1), elastin, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1), and TIMP-2, as well as decreased expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9). Our results indicate that the EtOAc fraction from A. tabularis root has considerable potential as a multifunctional cosmetic.
Keywords: Astilboides tabularis (Hemsl.) Engl.; antiwrinkle; ethyl acetate; moisturizing; skin whitening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


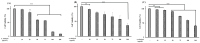









Similar articles
-
The in cellular and in vivo melanogenesis inhibitory activity of safflospermidines from Helianthus annuus L. bee pollen in B16F10 murine melanoma cells and zebrafish embryos.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 24;20(6):e0325264. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325264. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40554513 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory activity of soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) Cell Culture Extract on tyrosinase activity and melanin formation in alpha-melanocyte stimulating Hormone-Induced B16-F10 melanoma cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Aug;49(8):7827-7836. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07608-6. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35733058
-
Neurog1-Derived Peptides RMNE1 and DualPep-Shine Penetrate the Skin and Inhibit Melanin Synthesis by Regulating MITF Transcription.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 24;24(7):6158. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076158. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047130 Free PMC article.
-
The melanin inhibitory effect of plants and phytochemicals: A systematic review.Phytomedicine. 2022 Dec;107:154449. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154449. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36126406
-
Natural sources of melanogenic inhibitors: A systematic review.Int J Cosmet Sci. 2022 Apr;44(2):143-153. doi: 10.1111/ics.12763. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35048395
References
-
- Ahn D.K. Illustrated Book of Korean Medicinal Herbs. Kyo-Hak Publishing Co.; Seoul, Republic of Korea: 2003. p. 811.
-
- Yoon Y.S., Kim K.A., Yoo K.O. Environmental characteristics of Astilboides tabularis (Hemsl.) Engl. habitats. Korean J. Plant Resour. 2015;28:64–78. doi: 10.7732/kjpr.2015.28.1.064. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

