The SGLT2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin Mitigates the Harmful Effects of Methylglyoxal Exposure on Ovalbumin-Induced Mouse Airway Inflammation
- PMID: 40565216
- PMCID: PMC12193618
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125753
The SGLT2 Inhibitor Empagliflozin Mitigates the Harmful Effects of Methylglyoxal Exposure on Ovalbumin-Induced Mouse Airway Inflammation
Abstract
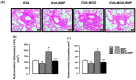
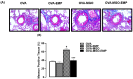
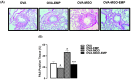
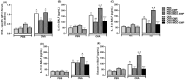
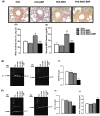
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory airway disease that can be aggravated by metabolic comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) and obesity. Elevated levels of methylglyoxal (MGO), a reactive glycolysis byproduct, have been associated with exacerbation of allergic airway disease. SGLT2 inhibitors have been successfully employed in DM2 treatment. Here, we hypothesized that elimination of MGO might be a potential anti-inflammatory mechanism of SGLT2 inhibitors. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of empagliflozin on ovalbumin (OVA)-induced airway inflammation in mice chronically exposed to MGO. Male C57BL/6 mice sensitized with OVA were exposed to 0.5% MGO for 12 weeks and treated with empagliflozin (10 mg/kg, gavage, two weeks). MGO exposure significantly enhanced airway eosinophil infiltration, mucus production and collagen deposition, as well as levels of IL-4, IL-5, eotaxin and TNF-α. Empagliflozin treatment significantly reduced OVA-induced airway disease, which was accompanied by reductions in IgE, IL-4, IL-5, eotaxin, and TNF-α levels. Empagliflozin significantly reduced the MGO levels in serum, and immunohistochemical staining, and protein expression of MGO-hydroimidazolone (MG-H1), while increasing IL-10 levels and glyoxylase-1 (GLO 1) activity in lungs. In conclusion, empagliflozin efficiently removes MGO from circulation, while increasing the MGO detoxification by GLO 1, thereby mitigating the OVA-induced inflammation in MGO-exposed mice.
Keywords: MG-H1; asthma; collagen; cytokines; glyoxalase; mucus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

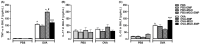
Similar articles
-
Gasdermin D silencing alleviates airway inflammation and remodeling in an ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mouse model.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jun 7;15(6):400. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06777-5. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38849380 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on cardiovascular events, death, and major safety outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016 May;4(5):411-9. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)00052-8. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27009625
-
Empagliflozin and liraglutide ameliorate HFpEF in mice via augmenting the Erbb4 signaling pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Aug;45(8):1604-1617. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01265-0. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38589689 Free PMC article.
-
Santonin attenuates Ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation by inhibiting IL-4/IL-13 signaling.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Sep 1;777:152284. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.152284. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40616980
-
Evaluating the costs of glycemic response with canagliflozin versus dapagliflozin and empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the United Arab Emirates.Curr Med Res Opin. 2017 Jun;33(6):1155-1163. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2017.1310091. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Curr Med Res Opin. 2017. PMID: 28323512
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

