miR-7-5p and Importin-7 Regulate the p53 Dynamics and Stability in Malignant and Benign Thyroid Cells
- PMID: 40565276
- PMCID: PMC12192917
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125813
miR-7-5p and Importin-7 Regulate the p53 Dynamics and Stability in Malignant and Benign Thyroid Cells
Abstract
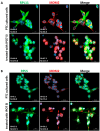
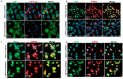
Thyroid carcinogenesis has multiple hallmarks, including evasion of tumor suppressors. Reactivation of wild-type p53 function is the ultimate goal in cancer therapy, which requires an understanding of the p53 suppression mechanism specific to the cancer type. MiR-7-5p and IPO7 are implicated in the pathogenesis of several human diseases. This work aims to investigate the role of miR-7-5p and IPO7 in p53 regulation in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) cells. Primary cultured thyroid cells and FFPE thyroid tissues from PTC and benign cases were used. Functional experiments were performed by transfection with IPO7 siRNA or miR-7-5p mimic/inhibitor, followed by apoptosis and luciferase reporter assays, immunoblot assays, and RT-PCR. The expression and subcellular localization of IPO7, p53, MDM2, and ribosomal proteins (RPL11 and RPL5) were studied by immunofluorescence staining and confocal microscopy. The results show that IPO7 is overexpressed in PTC and regulated by miR-7-5p. Modulation of IPO7 expression in cultured thyroid cells altered the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of p53, MDM2, RPL11, and RPL5, in addition to the p53 protein level and activity. The expression pattern of IPO7, p53, and MDM2 in cultured thyroid cells and clinical thyroid tissue specimens confirmed the association between IPO7 overexpression and reduced p53 stability in PTC. In conclusion, the data here show that p53 level and activity are differentially controlled in malignant and benign thyroid cells through miR-7-5P/IPO7-mediated regulation of RP-MDM2-p53 nucleocytoplasmic trafficking. In PTC, downregulation of miR-7-5p with consequent overexpression of IPO7 might be a protective mechanism used by cancer cells to evade p53 growth suppression during carcinogenesis.
Keywords: MDM2; PTC; importin 7; miR-7-5p; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- American Cancer Society Key Statistics for Thyroid Cancer. Cancer.org|1.800.227.2345. [(accessed on 31 January 2024)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/thyroid-cancer/about/key-statistics.....
-
- Vuong H.G., Altibi A.M., Abdelhamid A.H., Ngoc P.U., Quan V.D., Tantawi M.Y., Elfil M., Vu T.L., Elgebaly A., Oishi N., et al. The changing characteristics and molecular profiles of papillary thyroid carcinoma over time: A systematic review. Oncotarget. 2017;8:10637–10649. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12885. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

