Cyclodextrin-Modified Capillary Zone Electrophoresis for the Chiral Analysis of Proline and Hydroxyproline Stereoisomers in Chicken Collagen Hydrolysates
- PMID: 40565295
- PMCID: PMC12192952
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125832
Cyclodextrin-Modified Capillary Zone Electrophoresis for the Chiral Analysis of Proline and Hydroxyproline Stereoisomers in Chicken Collagen Hydrolysates
Abstract
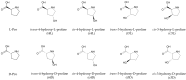
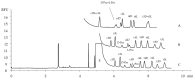
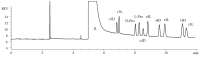
The stability of collagen, the most abundant protein in humans and many animals, is related to the hydroxylation of L-proline, a post-translational modification occurring at carbon 3 and 4 on its pyrrolidine ring. Collagens of different origins have shown different proline hydroxylation levels, making hydroxyprolines useful biomarkers in structure characterizations. The presence of two chiral carbon atoms, 3-hydroxyproline and 4-hydroxyproline, results in eight stereoisomers (four pairs of enantiomers) whose quantitation in collagen hydrolysates requires enantioselective analytical methods. Capillary electrophoresis was applied for the separation and quantitation of the eight stereoisomers of 3- and 4-hydroxyproline and D,L-proline in collagen hydrolysates. The developed method is based on the derivatization with the chiral reagent (R)-(-)-4-(3-Isothiocyanatopyrrolidin-yl)-7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole, enabling the use of a light-emitting diode-induced fluorescence detector for high sensitivity. The separation of the considered compounds was accomplished in less than 10 min, using a 500 mM acetate buffer pH 3.5 supplemented with 5 mM of heptakis(2,6-di-O-methyl)-β-cyclodextrin as the chiral selector. The method was fully validated and showed the adequate sensitivity for the application to samples of collagen hydrolysates. The analysis of samples extracted from chicken Pectoralis major muscles affected by growth-related myopathies showed different stereoisomer patterns compared to those from the unaffected control samples.
Keywords: capillary electrophoresis; chiral separations; collagen; cyclodextrins; derivatization; fast-growing chickens; fluorescent detection; hydroxyprolines; spaghetti meat; wooden breast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

