Brain Endothelial Cells in Blood-Brain Barrier Regulation and Neurological Therapy
- PMID: 40565303
- PMCID: PMC12193000
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125843
Brain Endothelial Cells in Blood-Brain Barrier Regulation and Neurological Therapy
Abstract
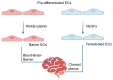
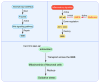
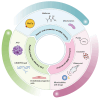
Brain endothelial cells (BECs) constitute the core component of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), regulating substance exchange between blood and the brain parenchyma to maintain central nervous system homeostasis. In pathological states, the BBB exhibits the disruption of tight junctions, endothelial cell (EC) damage, and increased permeability, accompanied by neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and abnormal molecular signaling pathways, leading to neurotoxic effects in the brain parenchyma and exacerbating neurodegeneration and disease progression. This review systematically summarizes the developmental origin, structural characteristics, and pathological mechanisms of BECs in diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, stroke, and glioblastoma with a particular focus on the regulatory mechanisms of the Wnt/β-catenin and VEGF signaling pathways. By integrating the latest research advances, this review aims to provide a comprehensive perspective for understanding the role of BECs in physiological and pathological states and to provide a theoretical basis for the development of BBB-based therapeutic approaches for neurological diseases.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier; brain endothelial cells; neurological disorders; signaling pathways; therapeutic strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Torices S., Teglas T., Naranjo O., Fattakhov N., Frydlova K., Cabrera R., Osborne O.M., Sun E., Kluttz A., Toborek M. Occludin Regulates HIV-1 Infection by Modulation of the Interferon Stimulated OAS Gene Family. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023;60:4966–4982. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03381-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

