A Review of Silica-Based Nanoplatforms for Anticancer Cargo Delivery
- PMID: 40565310
- PMCID: PMC12192846
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125850
A Review of Silica-Based Nanoplatforms for Anticancer Cargo Delivery
Abstract
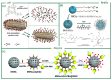
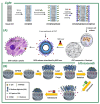
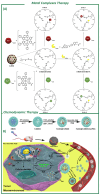
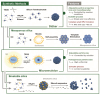
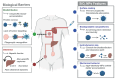
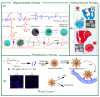
Stimuli-responsive silica nanoparticles have emerged as a promising platform for the targeted and controlled delivery of therapeutic agents in cancer therapy. These nanoparticles possess unique physicochemical properties that allow for the stimuli-triggered release of loaded cargos, such as drugs, enzymes, oligonucleotides, photosensitizers, and metals. The stimuli-responsive nature of these nanoparticles enables them to respond to specific internal and external signals within the tumor microenvironment, including pH, temperature, and redox potential, among others. This leads to the enhanced targeting of cancer cells and improved therapeutic efficacy while minimizing the off-target effects. This review highlights recent advances in the development and application of stimuli-responsive silica nanoparticles for the delivery of multiple active agents for cancer therapy. Overall, stimuli-responsive silica nanoparticles offer great potential for the development of more effective cancer therapies with improved selectivity and reduced side effects.
Keywords: cancer therapy; drug delivery; enzyme; mesoporous; metals; oligonucleotides; silica; stimuli responsive; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Breaking barriers with pH-responsive nanocarriers: a new frontier in precision oncology.Int J Pharm. 2025 Sep 15;682:125931. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125931. Epub 2025 Jul 7. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40633600 Review.
-
A Review on the Recent Advancements of Polymer-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Under Stimuli-Trigger.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;17(12):1640. doi: 10.3390/polym17121640. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40574168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the development of chitosan based nanocarriers for drug delivery application: Critical challenges, outlooks and promises in cancer therapy.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Sep;321(Pt 1):146184. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.146184. Epub 2025 Jul 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40692051 Review.
-
The multifunctional role of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as an emerging tool in tumor therapy.Acta Biomater. 2025 Jun 15;200:87-114. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.05.019. Epub 2025 May 13. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40374135 Review.
-
Tumor Microenvironment-Responsive Nanoparticles: Promising Cancer PTT Carriers.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 23;20:7987-8001. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S526497. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40584786 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- He S., Pan H., Zhang J. Advances of Typical Mesoporous Materials and the Application in Drug Delivery. Mater. Res. Express. 2023;10:042001. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/acc82d. - DOI
-
- Sivamaruthi B.S., Kapoor D.U., Kukkar R.R., Gaur M., Elossaily G.M., Prajapati B.G., Chaiyasut C. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Types, Synthesis, Role in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease, and Other Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15:2666. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122666. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jafari S., Maleki-Dizaji N., Barar J., Barzegar-Jalali M., Rameshrad M., Adibkia K. Methylprednisolone Acetate-Loaded Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles as a Potential Drug Delivery System for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016;91:225–235. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2016.05.014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

