Long Non-Coding RNA LOC401312 Induces Radiosensitivity Through Upregulation of CPS1 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 40565327
- PMCID: PMC12193141
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125865
Long Non-Coding RNA LOC401312 Induces Radiosensitivity Through Upregulation of CPS1 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
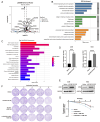
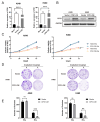
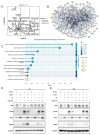
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), non-protein-coding transcripts exceeding 200 nucleotides, are critical regulators of gene expression through chromatin remodeling, transcriptional modulation, and post-transcriptional modifications. While ionizing radiation (IR) induces cellular damage through direct DNA breaks, reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated oxidative stress, and bystander effects, the functional involvement of lncRNAs in the radiation response remains incompletely characterized. Here, through genome-wide CRISPR activation (CRISPRa) screening in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells, we identified LOC401312 as a novel radiosensitizing lncRNA, the stable overexpression of which significantly enhanced IR sensitivity. Transcriptomic profiling revealed that LOC401312 transcriptionally upregulates carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1 (CPS1), a mitochondrial enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis. Notably, CPS1 overexpression recapitulated the radiosensitization phenotype observed with LOC401312 activation. Mechanistic investigations revealed that CPS1 suppresses the phosphorylation of ATM kinase (Ser1981) protein, which is a key mediator of DNA damage checkpoint activation. This study established the LOC401312-CPS1-ATM axis as a previously unrecognized regulatory network governing radiation sensitivity, highlighting the potential of lncRNA-directed metabolic rewiring to impair DNA repair fidelity. Our findings not only expand the functional landscape of lncRNAs in DNA damage response but also provide a therapeutic rationale for targeting the LOC401312-CPS1 axis to improve radiotherapy efficacy in NSCLC.
Keywords: CPS1; CRISPRa screening; LOC401312; ionizing radiation sensitivity regulation; long noncoding RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Derrien T., Johnson R., Bussotti G., Tanzer A., Djebali S., Tilgner H., Guernec G., Martin D., Merkel A., Knowles D.G., et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012;22:1775–1789. doi: 10.1101/gr.132159.111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

