Molecular Insights into the Diagnosis of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Beyond Morphology and Immunophenotype
- PMID: 40565334
- PMCID: PMC12192600
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125871
Molecular Insights into the Diagnosis of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Beyond Morphology and Immunophenotype
Abstract
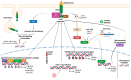
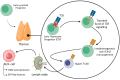
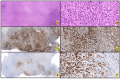
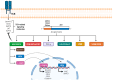
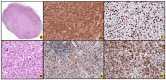
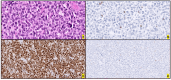
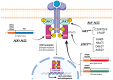
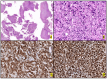
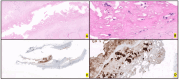
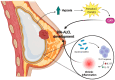
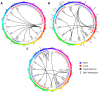
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) represents a diverse group of mature T-Cell Lymphomas unified by strong CD30 expression but with different molecular and clinical subtypes. This review summarizes recent molecular advances in ALCL, highlighting key discoveries that have refined its classification, diagnosis, and therapeutic strategies. ALCL comprises four major entities: systemic ALK-positive ALCL, systemic ALK-negative ALCL, Breast Implant-Associated ALCL (BIA-ALCL), and primary cutaneous ALCL. Each subtype exhibits unique phenotypes, along with cytogenetic and molecular alterations that affect clinical outcomes. Nevertheless, different oncogenic mechanisms mediate STAT3 activation. In ALK-positive ALCL, ALK fusion proteins drive oncogenesis via constitutive activation of STAT3 and other signaling pathways. ALK-negative ALCL comprises heterogeneous genetic subtypes, in which JAK/STAT3 pathway alterations and novel gene fusions are gaining recognition as potential therapeutic targets. This review emphasizes the need for integrative molecular diagnostics to improve stratification of ALCL subtypes and targeted treatment approaches. Future research should focus on elucidating the biological mechanisms underlying these alterations and on translating molecular insights into clinical practice.
Keywords: ALK; Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma; BIA-ALCL; DUSP22; STAT3; TP63; pcALCL.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Harris N., Jaffe E., Stein H., Banks P., Chan J., Cleary M., Delsol G., De Wolf- Peeters C., Falini B., Gatter K. A Revised European-American Classification of Lymphoid Neoplasms: A Proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group [See Comments] Blood. 1994;84:1361–1392. doi: 10.1182/blood.V84.5.1361.1361. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pulford K., Lamant L., Morris S.W., Butler L.H., Wood K.M., Stroud D., Delsol G., Mason D.Y. Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) and Nucleolar Protein Nucleophosmin (NPM)-ALK Proteins in Normal and Neoplastic Cells with the Monoclonal Antibody ALK1. Blood. 1997;89:1394–1404. doi: 10.1182/blood.V89.4.1394. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

