Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Evaluation of Aqueous Extracts from Hymenochaetaceae Fungi Associated with Endemic Chilean Sclerophyll Forest Trees
- PMID: 40565340
- PMCID: PMC12193641
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26125877
Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Evaluation of Aqueous Extracts from Hymenochaetaceae Fungi Associated with Endemic Chilean Sclerophyll Forest Trees
Abstract
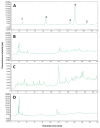
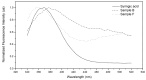
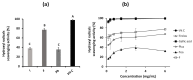
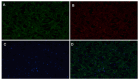
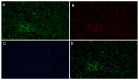
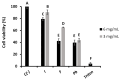
In the search for safe and effective natural antioxidants, this study investigates the antioxidant and cytotoxic properties of aqueous extracts obtained from three fungi of the family Hymenochaetaceae: Inonotus sp., Fulvifomes sp., and Phylloporia boldo, all associated with endemic trees of the Chilean sclerophyll forest. Antioxidant capacity was assessed through DPPH, ABTS, and hydroxyl radical scavenging assays. Fulvifomes sp. exhibited the highest antioxidant activity across all methods, which was consistent with its elevated polyphenol content. P. boldo, on the other hand, had the highest protein concentration but comparatively lower antioxidant activity. Cytotoxicity was evaluated using the WST-1 assay in the RTgill-W1 salmonid cell line, revealing that Inonotus sp. displayed the lowest cytotoxicity at both tested concentrations, suggesting it may be suitable for bioactive applications in aquaculture. In contrast, Fulvifomes sp. and P. boldo showed significant cytotoxic effects at higher concentrations. These findings highlight the potential of Inonotus sp. as a natural antioxidant with low cytotoxicity and encourages further exploration of native forest fungi as sources of functional bioactive compounds for food, nutraceutical, or aquaculture applications.
Keywords: Fulvifomes sp.; Hymenochaetaceae fungi; Inonotus sp.; Phylloporia boldo; antioxidant activity; aqueous extracts; cytotoxicity; in vitro assays; polyphenols; sclerophyll forest.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Oxidative Stress Protection and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Polyphenolic Fraction from Urtica dioica: In Vitro Study Using Human Skin Cells.Molecules. 2025 Jun 9;30(12):2515. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122515. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572482 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of epoetin alpha, epoetin beta and darbepoetin alpha in anaemia associated with cancer, especially that attributable to cancer treatment.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Apr;11(13):1-202, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta11130. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17408534
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Berglund H., Jönsson M.T., Penttilä R., Vanha-Majamaa I. The Effects of Burning and Dead-Wood Creation on the Diversity of Pioneer Wood-Inhabiting Fungi in Managed Boreal Spruce Forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011;261:1293–1305. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2011.01.008. - DOI
-
- Guerra F., Badilla L., Cautín R., Castro M. In Vitro Propagation of Peumus Boldus Mol, a Woody Medicinal Plant Endemic to the Sclerophyllous Forest of Central Chile. Horticulturae. 2023;9:1032. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae9091032. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

