Leg Length Discrepancy After Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Review of Clinical Assessments, Imaging Diagnostics, and Medico-Legal Implications
- PMID: 40565385
- PMCID: PMC12193556
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13121358
Leg Length Discrepancy After Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Review of Clinical Assessments, Imaging Diagnostics, and Medico-Legal Implications
Abstract
Background/objectives: Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is a widely performed procedure to alleviate pain and improve function in patients with hip disorders. However, leg length discrepancy (LLD) remains a prevalent complication. LLD can cause gait disturbances, back pain, postural imbalance, and patient dissatisfaction, along with significant medico-legal implications. This review examines the evaluation, management, and medico-legal aspects of LLD.
Methods: The review analyzed literature on the prevalence, evaluation methods, and management strategies for LLD in THA. Radiographic and clinical assessment tools were considered, alongside factors such as pelvic obliquity and pre-existing conditions. The importance of preoperative planning, intraoperative techniques (including computer-assisted methods), and comprehensive documentation was evaluated to address both clinical and legal challenges.
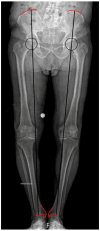
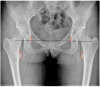
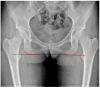
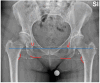
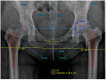
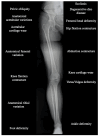
Results: The review shows that leg length discrepancy (LLD) following total hip arthroplasty (THA) occurs in 3% to 30% of cases, with mean values ranging from 3 to 17 mm. LLD may result from anatomical or procedural factors, and effective evaluation requires both radiographic imaging and clinical assessment. Preoperative planning plays a critical role in accurately assessing anatomical parameters and selecting appropriate prosthetic components to preserve or restore limb length symmetry. Advanced intraoperative techniques, including computer-assisted surgery, help reduce LLD incidence. While some complications may be unavoidable, proper documentation and patient communication, particularly regarding informed consent, are essential to mitigate medico-legal risks Conclusions: LLD after THA requires a multidimensional approach incorporating clinical, radiological, biomechanical, and legal considerations. Effective preoperative and intraoperative strategies, combined with robust communication and documentation, are essential to minimize LLD and its associated risks. A focus on precision and patient-centered care can improve outcomes and reduce litigation.
Keywords: leg length discrepancy; medico-legal implications; total hip arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson C.G., Jang S.J., Brilliant Z.R., Mayman D.J., Vigdorchik J.M., Jerabek S.A., Sculco P.K. Complication Rate After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Using the Posterior Approach and Enabling Technology: A Consecutive Series of 2888 Hips. J. Arthroplast. 2023;38:S119–S123.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2023.04.029. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lecoanet P., Vargas M., Pallaro J., Thelen T., Ribes C., Fabre T. Leg length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty: Can leg length be satisfactorily controlled via anterior approach without a traction table? Evaluation in 56 patients with EOS 3D. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2018;104:1143–1148. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2018.06.020. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

