Physical Activity and Sedentary Patterns of Pregnant Women in Southern Spain and the Relationship with Sociodemographic and Obstetric Characteristics: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 40565450
- PMCID: PMC12192721
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13121423
Physical Activity and Sedentary Patterns of Pregnant Women in Southern Spain and the Relationship with Sociodemographic and Obstetric Characteristics: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
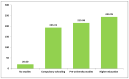
Background/Objectives: Physical activity (PA) during pregnancy presents health benefits for mother and child. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends at least 150 min of moderate-intensity physical activity per week for a healthy pregnancy. The objectives of this study were to describe physical and sedentary activity patterns, estimate the proportion of women meeting PA recommendations, and identify associated sociodemographic and obstetric characteristics in a sample of pregnant women from southern Spain. Methods: For this cross-sectional study, a random sample of 385 pregnant women attending their 20th-week scheduled ultrasound at their referral hospital was selected. Inclusion criteria were being between 18 and 22 gestational weeks pregnant and communicating in Spanish. A face-to-face structured interview was used to collect demographic, obstetric, and PA data, as well as sedentary patterns. Indexes of weekly PA in various domains were computed. Bivariate analyses were conducted to assess the variability of physical and sedentary activities according to sociodemographic and obstetric variables. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Results: A total of 84.4% of participants engaged in some type of PA and 73.7% met WHO PA requirements. Higher leisure PA was associated with higher education (p < 0.05) and first-time pregnancy (p < 0.01). Higher work PA was linked to lower education (p < 0.01), being born outside Spain (p < 0.05), and later pregnancy awareness (p < 0.01). Higher sedentary daily time was associated with higher education (p < 0.01), speaking Spanish as a child (p < 0.05), and first-time pregnancy (p < 0.05). Conclusions: Most pregnant women in this study met PA recommendations. Correlates of leisure PA differ from those regarding work PA.
Keywords: Spain; correlates; guidelines; patterns; physical activity; pregnancy; sedentary behaviour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interventions for promoting habitual exercise in people living with and beyond cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 19;9(9):CD010192. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010192.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30229557 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
-
Metformin for women who are overweight or obese during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 24;7(7):CD010564. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010564.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30039871 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of exercise referral schemes: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Dec;15(44):i-xii, 1-254. doi: 10.3310/hta15440. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 22182828 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

