The Treatment of Psychotic and Bipolar Disorders Within the South African Context: Perspectives of a Clinical Pharmacist
- PMID: 40565483
- PMCID: PMC12193330
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13121456
The Treatment of Psychotic and Bipolar Disorders Within the South African Context: Perspectives of a Clinical Pharmacist
Abstract
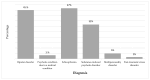
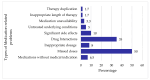
Background: The effective management of psychotic and bipolar disorders in tertiary care can improve patient outcomes, yet the role of clinical pharmacists in optimising psychotropic medication use remains underexplored in South Africa. This study aims to investigate the role and interventions of clinical pharmacists in managing psychotic and bipolar disorders within a tertiary hospital in South Africa. Methods: A quantitative, descriptive study was conducted among 60 adult patients admitted to the psychiatric and internal medicine wards diagnosed with psychotic and/or bipolar disorder. A previously validated, standardised pharmaceutical care form was utilised for a purposive sample of inpatient files. Medication-related problems were identified, and appropriate interventions were suggested. Prescriptions were also assessed for adherence to treatment guidelines, including the South African Standard Treatment Guidelines, the American Psychiatric Association guidelines, and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines. Results: The study included 60 patients (37 females) with a mean age of 37 years. Diagnoses included schizophrenia (28.8%), bipolar disorder (27.5%), and stimulant-induced psychosis (19.3%). Sixty-two medication-related problems were identified, leading to 77 proposed interventions, of which 65 were implemented. Among the prescriptions, 75% (n = 45) adhered to the South African Standard Treatment guidelines, 76% (n = 46) adhered to the NICE guidelines, and 71% (n = 43) adhered to the APA guidelines. Conclusions: Clinical pharmacists identified a number of medication-related problems in patients with psychotic and bipolar disorders, and their proposed interventions were largely accepted. The findings highlight the pharmacist's role in optimising medication therapy and adherence to guidelines, suggesting that improved treatment monitoring is necessary in this setting.
Keywords: South Africa; bipolar disorders; clinical pharmacists; medication-related problems; psychopharmacology; psychotic disorders; treatment guidelines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Interventions for patients and caregivers to improve knowledge of sickle cell disease and recognition of its related complications.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 6;10(10):CD011175. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011175.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27711980 Free PMC article.
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
-
Effect of pharmacist intervention on improving antidepressant medication adherence and depression symptomology: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Res Social Adm Pharm. 2018 Apr;14(4):321-331. doi: 10.1016/j.sapharm.2017.05.008. Epub 2017 May 22. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2018. PMID: 28622997
-
What is the value of routinely testing full blood count, electrolytes and urea, and pulmonary function tests before elective surgery in patients with no apparent clinical indication and in subgroups of patients with common comorbidities: a systematic review of the clinical and cost-effective literature.Health Technol Assess. 2012 Dec;16(50):i-xvi, 1-159. doi: 10.3310/hta16500. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 23302507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jain A., Mitra P. Bipolar Affective Disorder. Europe PMC; Cambridge, UK: 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources