Associations of Body Mass Index and Lifestyle Factors with Suicidal Ideation, Planning, and Attempts Among Korean Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 40565498
- PMCID: PMC12192561
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13121470
Associations of Body Mass Index and Lifestyle Factors with Suicidal Ideation, Planning, and Attempts Among Korean Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Unhealthy lifestyles constitute significant risk factors for adolescent suicide, and their detrimental effects may persist from adolescence into adulthood. This research study sought to examine how Body Mass Index (BMI), alongside various lifestyle behaviors among teenagers in Korea, correlates with suicidal thoughts, the formulation of suicide plans, and actual suicide attempts.
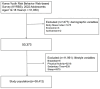
Methods: The research examined unprocessed information collected during the 2022 Korean Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey (KYRBS), which was administered by the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA). Lifestyle factors associated with suicidal behavior were selected as independent variables. The sample was stratified according to BMI for further analysis. Logistic regression models were applied to assess the association between lifestyle factors and the risk of adolescent suicide.
Results: The analysis identified significant correlations between unhealthy dietary patterns, hazardous drinking behavior, smoking, and a sleep duration of less than 5 h, all of which were associated with a heightened suicide risk among adolescents. Notably, underweight adolescents who had a sleep duration of less than 5 h demonstrated a markedly elevated risk of suicidal ideation (OR = 2.391, 95% CI [1.035-5.525]). Among overweight adolescents, frequent coffee consumption was significantly associated with both suicidal planning (OR = 1.850, 95% CI [1.133-3.020]) and suicide attempts (OR = 1.958, 95% CI [1.024-3.742]). Importantly, hazardous drinking behavior was strongly associated with suicide attempts (OR = 2.277, 95% CI [1.132-4.580]). Non-smoking behavior exhibited a significant relationship with a decreased likelihood of suicidal ideation (OR = 0.706, 95% CI [0.507-0.983]) and suicidal planning (OR = 0.528, 95% CI [0.299-0.930]). Furthermore, among obese adolescents, non-smoking behavior significantly decreased the risk of suicidal ideation compared to smoking (OR = 0.514, 95% CI [0.297-0.887]).
Conclusions: The study revealed that the combined impact of unhealthy behaviors-smoking, eating an unhealthy breakfast, sleeping for less than 5 h, and hazardous drinking behavior-significantly affect suicide-related behaviors in adolescents. The interaction between BMI and lifestyle factors is a critical determinant of these behaviors. Specifically, sleep health exerts a substantial influence on suicide-related behaviors in underweight adolescents, while smoking strongly correlates with suicidal behaviors in overweight and obese adolescents. Targeted attention to the interplay of smoking, diet, sleep, and alcohol consumption with BMI is crucial for the early detection and prevention of adolescent suicide.
Keywords: adolescents; body mass index; cross-sectional study; health behaviors; lifestyle; suicide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Obesity—Our World in Data. [(accessed on 7 November 2023)]. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/obesity.
-
- KDCA KDCA. [(accessed on 3 May 2024)]. Available online: https://www.kdca.go.kr.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources