Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of PP2C Gene Family in Eelgrass
- PMID: 40565549
- PMCID: PMC12193245
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16060657
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of PP2C Gene Family in Eelgrass
Abstract
Background: Protein Phosphatase 2C (PP2C), a conserved family in plants, plays a crucial role in ABA and MAPK signaling pathways. Its functional diversity provides key mechanisms for plants' adaptation to environmental changes. However, research on PP2C family members remains significantly underexplored in seagrasses, which are model organisms adapted to complex marine environments.
Methods: In this study, we systematically analyzed the PP2C gene family in eelgrass using bioinformatic methods and performed a qPCR experiment to verify the expression of a few members in their response to salt stress.
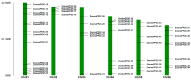
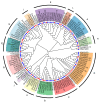
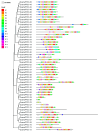
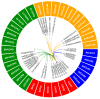
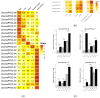
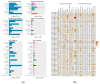
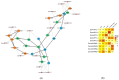
Results: The eelgrass PP2C gene family comprises 52 members, categorized into 13 subfamilies. Most PP2C genes exhibit a differential expression across various organs, with some members showing significant organ specificity. For instance, 12 members are specifically highly expressed in male flowers, suggesting that PP2Cs may function in male flower development. Additionally, four members (ZosmaPP2C-04, ZosmaPP2C-07, ZosmaPP2C-15, and ZosmaPP2C-18) in eelgrass are up-regulated under salt stress, with a qPCR confirming their response. The syntenic genes of ZosmaPP2C-15 and ZosmaPP2C-18 were identified across multiple species, indicating their evolutionary conservation. Numerous response elements associated with plant hormones and stress were identified within the promoter sequences of eelgrass PP2C genes. Notably, the promoter regions of salt-responsive genes are rich in the ABRE, implying that ABA may participate in regulating the expression of these PP2Cs. Furthermore, the predictive analysis of protein interactions suggests the potential existence of the ABA core signaling module PYL-PP2C-SnRK2 in eelgrass.
Conclusions: This study provides a new insight for understanding the biological functions of the PP2C family in eelgrass, which is important for elucidating the mechanisms of its growth, development, and environmental adaptability.
Keywords: ABA; PP2C; eelgrass; male flower; salt stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide characterization of GRAS gene family and their expression profiles under diverse biotic and abiotic stresses in Amorphophallus konjac.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 8;26(1):643. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11777-6. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40629278 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the DnaJ gene family and their expression profiles under salt stress in potato.BMC Genomics. 2025 Aug 19;26(1):758. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11961-8. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40830829 Free PMC article.
-
Genome identification of NAC gene family and its gene expression patterns in responding to salt and drought stresses in Rhododendron delavayi.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 17;25(1):924. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06965-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40676511 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted roles of PP2C phosphatases in plant growth, signaling, and response to abiotic and biotic stress.Plant Commun. 2025 Jul 12:101457. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2025.101457. Online ahead of print. Plant Commun. 2025. PMID: 40652328 Review.
-
Factors that influence parents' and informal caregivers' views and practices regarding routine childhood vaccination: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 27;10(10):CD013265. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013265.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34706066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Umezawa T., Sugiyama N., Mizoguchi M., Hayashi S., Myouga F., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Ishihama Y., Hirayama T., Shinozaki K. Type 2C Protein Phosphatases Directly Regulate Abscisic Acid-Activated Protein Kinases in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:17588–17593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907095106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- LJKQZ20222354/the Fund of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education
- LJ212410158026/the Fund of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education
- 2024JBYBZ003/the Fund of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education
- C2022204088/the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Hebei for Excellent Young Scholar
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

