Deficiency in KPNA4, but Not in KPNA3, Causes Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder like Symptoms in Mice
- PMID: 40565582
- PMCID: PMC12193263
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16060690
Deficiency in KPNA4, but Not in KPNA3, Causes Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder like Symptoms in Mice
Abstract
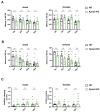
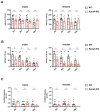
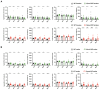
Nucleocytoplasmic transport is crucial for neuronal cell physiology and defects are involved in neurodegenerative diseases like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease, but also in ageing. Recent studies have suggested, that the classic nuclear import factor adapters KPNA3 (also named importin alpha4) and KPNA4 (also named importin alpha3) could be associated with the development of motor neuron diseases, a condition specifically affecting the neurons projecting from brain to spinal cord or from spinal cord to the muscles. Here we set out to analyze the neuronal function of mice deficient in KPNA3 (Kpna3-KO) or KPNA4 (Kpna4-KO). The motoric abilities and locomotion at different time points in ageing were tested to study the role of these two genes on motor neuron function. While we did not find deficits related to motor neurons in both mouse models, we discovered a hypermotoric phenotype in KPNA4-deficient mice. Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is caused by a combination of genetic, environmental and neurobiological factors and a number of genes have been suggested in genome-wide association studies to contribute to ADHD, including KPNA4. Here we provide supportive evidence for KPNA4 as a candidate pathogenic factor in ADHD, by analysing Kpna4-KO mice which show ADHD-like symptoms.
Keywords: ADHD; hyperactivity; importin; karyopherin; motor neuron disease; nucleocytoplasmic transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parent training interventions for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children aged 5 to 18 years.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 7;2011(12):CD003018. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003018.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 22161373 Free PMC article.
-
Bupropion for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 2;10(10):CD009504. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009504.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28965364 Free PMC article.
-
Methylphenidate for children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 21;11(11):CD011144. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011144.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29159857 Free PMC article.
-
Methylphenidate for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents - assessment of adverse events in non-randomised studies.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 9;5(5):CD012069. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012069.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29744873 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulant and non-stimulant drug therapy for people with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and epilepsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 13;7(7):CD013136. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013136.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35844168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kinoshita Y., Ito H., Hirano A., Fujita K., Wate R., Nakamura M., Kaneko S., Nakano S., Kusaka H. Nuclear contour irregularity and abnormal transporter protein distribution in anterior horn cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009;68:1184–1192. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181bc3bec. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

