The Role of Adiponectin and ADIPOQ Variation in Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40565591
- PMCID: PMC12193251
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16060699
The Role of Adiponectin and ADIPOQ Variation in Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review
Abstract
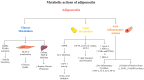
Metabolic syndrome (MetS), a significant global health concern, is characterized as a cluster of metabolic abnormalities that elevate the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Adiponectin, an adipokine secreted by adipose tissue, plays a crucial role in regulating glucose and lipid homeostasis while exhibiting protective effects against vascular alterations. Single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) in the ADIPOQ gene have significantly affected circulating adiponectin levels and metabolic parameters. This narrative review examines current evidence on the relationship between adiponectin, ADIPOQ gene variants, and metabolic syndrome. The findings indicate that lower adiponectin levels are associated with an increased risk of metabolic syndrome components, including elevated triglycerides (TGs), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and fasting glucose levels. In conclusion, adiponectin emerges as a key regulator of metabolic homeostasis, with SNVs in the ADIPOQ gene correlating with the development of metabolic-related complications.
Keywords: ADIPOQ gene; adiponectin; metabolic syndrome; obesity; single-nucleotide variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adiponectin GWAS loci harboring extensive allelic heterogeneity exhibit distinct molecular consequences.PLoS Genet. 2020 Sep 11;16(9):e1009019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009019. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32915782 Free PMC article.
-
Association of a polymorphic variant of the adiponectin gene with insulin resistance in african americans.Clin Transl Sci. 2008 Dec;1(3):194-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2008.00055.x. Clin Transl Sci. 2008. PMID: 20443850 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Endocrine Disorders on Lipids and Lipoproteins.2023 Apr 6. In: Feingold KR, Ahmed SF, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, Muzumdar R, Purnell J, Rey R, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. 2023 Apr 6. In: Feingold KR, Ahmed SF, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, Muzumdar R, Purnell J, Rey R, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. PMID: 28121116 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
What is the relationship between exercise and metabolic abnormalities? A review of the metabolic syndrome.Sports Med. 2004;34(6):371-418. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200434060-00004. Sports Med. 2004. PMID: 15157122
-
Associations of Estrogen Receptor Alpha Gene Polymorphisms with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Horm Metab Res. 2018 Jun;50(6):469-477. doi: 10.1055/a-0620-8553. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Horm Metab Res. 2018. PMID: 29883973
References
-
- Sorout J., Kacker S., Saboo N. Metabolic Syndrome and Possible Treatments (Consecutive Therapies): A Literature Review. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2022;18:351–357. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.18.6.2022.1206. - DOI
-
- Gupta A., Gupta V. Metabolic Syndrome: What Are the Risks for Humans? Biosci. Trends. 2010;4:204–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

