Human CD36: Gene Regulation, Protein Function, and Its Role in Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis
- PMID: 40565598
- PMCID: PMC12192553
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16060705
Human CD36: Gene Regulation, Protein Function, and Its Role in Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis
Abstract
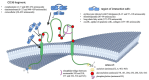
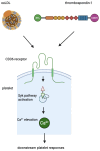
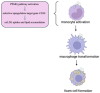
Human CD36 plays an important role in ligand binding, signalling, cell adhesion, and the regulation of angiogenesis. As a scavenging receptor, it is responsible for clearing long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) and removing approximately 50% of oxidised low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) from plasma. The CD36 gene is alternatively spliced. It has several alternative promoters and first exons. The alternative transcripts are expressed in multiple tissues, and their expression patterns are highly variable. The molecular mechanisms that regulate CD36 gene expression are complex and reflect its multifunctional role in different tissues. CD36 activity has been linked to several metabolic processes, such as inflammation, angiogenesis, phagocytosis, and energy homeostasis. CD36 plays a key role in regulating vascular and cardiovascular health and in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. CD36 gene mutations in the Caucasian population are rare. Hence, it is extremely difficult to recruit a statistically significant group of CAD patients with these mutations. Nevertheless, this population is largely at risk of cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis is a multifactorial disease, but the role of the CD36 receptor in the development of ox-LDL is extremely important. This review aims to introduce readers to issues related to the relationship between CD36 and CAD. The activity of this receptor should be considered when exploring treatment options for atherosclerosis-related complications.
Keywords: CD36; atherosclerosis; ox-LDL receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous