Comparative Analysis of Nutritional, Textural, and Sensory Attributes of Butter Crab and Normal Female Mud Crab (Scylla paramamosain): Insights for Market Positioning and Consumer Preference
- PMID: 40565710
- PMCID: PMC12192415
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14122101
Comparative Analysis of Nutritional, Textural, and Sensory Attributes of Butter Crab and Normal Female Mud Crab (Scylla paramamosain): Insights for Market Positioning and Consumer Preference
Abstract
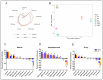
In recent years, the butter crab (BC), a distinctive phenotypic variant of the female mud crab Scylla paramamosain, has garnered increasing market attention due to its perceived superior nutritional and sensory attributes. This study conducted a comprehensive comparative analysis of the nutritional composition, textural properties, and sensory characteristics of BC and normal female mud crab (NFMC). Results showed that the muscle and hepatopancreas of BC contained significantly higher lipid contents (0.77 and 22.14 g/100 g wet weight) and elevated levels of DHA + EPA (18.36% and 12.86% of total fatty acids), which contributed to its characteristic orange-yellow coloration, as reflected by colorimetric values (L* × a* × b* = 30.20 × 4.38 × 16.15). Sensory evaluation revealed that BC exhibited enhanced umami taste and aroma in both muscle and hepatopancreas, corresponding to higher concentrations of umami amino acids (0.75 and 1.95 mg/g wet weight) and aldehydes (35.06% and 34.37% of total volatiles), respectively. In addition, 80% of panelists preferred BC based on visual appearance, indicating its strong consumer appeal. Overall, this study advances our understanding of the biochemical and sensory profiles of BC and NFMC and provides important insights for market positioning of BC in the premium seafood sector.
Keywords: butter crab; normal female mud crab; nutritional profiles; sensory characteristics; texture analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior and Purchasing Decisions Regarding Mud Crabs (Scylla paramamosain) in the Major Cities of Vietnam.Foods. 2025 Jun 23;14(13):2198. doi: 10.3390/foods14132198. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40646951 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Resequencing Provides Novel Insights Into the Genetic Diversity, Population Structure, and Patterns of Runs of Homozygosity in Mud Crab (Scylla paramamosain).Evol Appl. 2025 Sep 3;18(9):e70153. doi: 10.1111/eva.70153. eCollection 2025 Sep. Evol Appl. 2025. PMID: 40909995 Free PMC article.
-
Effective management of Mud crab Reovirus (MCRV) infection in mud crab, Scylla serrata (Forskal, 1775) culture, using an individual compartmentalized system.J Invertebr Pathol. 2025 Sep;212:108379. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2025.108379. Epub 2025 Jun 6. J Invertebr Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40482995
-
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD003725. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149418 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen B., Zheng J., Chen C., Wu K., Lin F., Ning L., Rong H., Wen X. Differences in lipid accumulation and mobilization in the hepatopancreas and ovary of female mud crab (Scylla paramamosain, Estampador, 1949) during ovarian development. Aquaculture. 2023;564:739046. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.739046. - DOI
-
- Liu C., Meng F., Tang X., Wang A., Pan Z. Comparison of nonvolatile taste active compounds of wild and cultured mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Fish. Sci. 2018;84:897–907. doi: 10.1007/s12562-018-1227-0. - DOI
-
- Fisheries Bureau of Agriculture Ministry of China . China Fishery Statistical Yearbook. China Agriculture Press; Beijing, China: 2024. pp. 20–22.
-
- Wang H., Tang L., Wei H., Mu C., Wang C. “Butter crab”: An environment-induced phenotypic variation of Scylla paramamosain with special nutrition and flavour. Aquac. Res. 2019;50:541–549. doi: 10.1111/are.13925. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

