Production Methods, Biological Activity and Potential Application Prospects of Astaxanthin
- PMID: 40565712
- PMCID: PMC12192321
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14122103
Production Methods, Biological Activity and Potential Application Prospects of Astaxanthin
Abstract
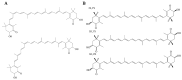
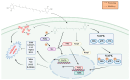
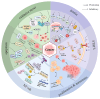
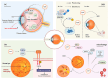
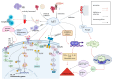
Astaxanthin (AST), a ketocarotenoid, is prevalent in aquatic life forms. AST has a variety of health-promoting effects, such as anti-oxidation, anti-cancer, eye protection, anti-inflammatory, immune regulation, skin care, anti-diabetes, neuroprotection, etc. It holds significant potential for applications in healthcare products, food additives, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and aquaculture. The production capacity of AST limits its wide application to a certain extent. The instability and safety risks associated with the chemical synthesis of AST have led to increased interest in its biosynthetic pathway. In this paper, the synthesis pathway, biological activity, and application prospects of AST were reviewed. To enhance the market accessibility of AST, investigating innovative synthesis techniques and its emergent biological effects is crucial.
Keywords: application prospects; astaxanthin; biological activity; ketocarotenoid; mechanisms; source.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Single-incision sling operations for urinary incontinence in women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 26;7(7):CD008709. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008709.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 27;10:CD008709. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008709.pub4. PMID: 28746980 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Deciphering the therapeutic potential of Sinigrin: A promising anti-inflammatory agent for chronic disease management.Phytomedicine. 2025 Aug;144:156875. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156875. Epub 2025 Jun 1. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40505485 Review.
References
-
- Deng Y., Zhan W., Xie S., Peng H., Cao H., Tang Z., Tian Y., Zhu T., Sun P., Jin M., et al. Multi-omics analysis revealed the effects of different astaxanthin sources on the antioxidant properties of Scylla paramamosain. Food Chem. 2025;478:143470. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.143470. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

