Assessment of Prehospital Care for Pediatric Patients with Thermal Injuries: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 40565809
- PMCID: PMC12194496
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14124063
Assessment of Prehospital Care for Pediatric Patients with Thermal Injuries: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
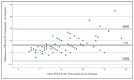
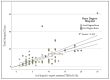
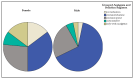
Background/Objectives: Accurate prehospital assessment of total body surface area burned (TBSA-B) is crucial for pediatric burn management, guiding resuscitation, fluid therapy, and transfer decisions. This study evaluates the accuracy of prehospital TBSA-B estimations compared to in-hospital expert assessment and examines their impact on prehospital management. Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 104 pediatric burn cases (median 17 months; 5 days-14 years) from 2017 to 2021. The primary endpoint was the difference between prehospital TBSA-B estimation and clinical measurement, with a clinically significant discrepancy defined as >5%. Secondary endpoints included the relationship between TBSA-B estimation and fluid therapy, analgesia, and hospital stay duration. Results: Prehospital TBSA-B estimations ranged from 2% to 40% (mean: 13.9%, SD = 4.4%) with scalds being the most common burn type (90.4%). Bland-Altman analysis showed a mean TBSA-B overestimation (bias) of 6.35%, with limits of agreement ranging from -6.97% (CI: -9.42 to -4.51) to 19.67% (CI: 17.21 to 22.12). No significant patterns in overestimation were associated with age, gender, or burn location. Fluid therapy volumes were independent of prehospital TBSA-B estimates, and analgesic administration varied by gender, with girls receiving less analgesia than boys, but showed no association with burn extent or severity. Hospital stay duration correlated proportionally with in-hospital assessed TBSA-B. Conclusions: Prehospital TBSA-B estimation was systematically overestimated, yet it did not influence fluid therapy decisions. Gender differences were observed in analgesic administration, while hospital stay duration was directly related to burn extent. These findings highlight the need for improved training and standardized tools to enhance prehospital burn assessment in pediatric patients.
Keywords: TBSA-B; anesthesiology; emergency medicine; pediatric; thermal injury; total body surface area burned.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Eich, Sinnig M., Guericke H. Akutversorgung Des Brandverletzten Kindes. Notf. Rettungsmedizin. 2014;17:113–122. doi: 10.1007/s10049-013-1809-4. - DOI
-
- Goverman J., Bittner E.A., Friedstat J.S., Moore M., Nozari A., Ibrahim A.E., Sarhane K.A., Chang P.H., Sheridan R.L., Fagan S.P. Discrepancy in Initial Pediatric Burn Estimates and Its Impact on Fluid Resuscitation. J. Burn. Care Res. 2015;36:574–579. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0000000000000185. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

