Quantitative Ultrasound Characterization of Intensity-Dependent Changes in Muscle Tissue During Percutaneous Electrolysis
- PMID: 40565810
- PMCID: PMC12194116
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14124064
Quantitative Ultrasound Characterization of Intensity-Dependent Changes in Muscle Tissue During Percutaneous Electrolysis
Abstract
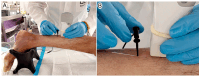
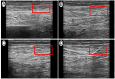
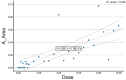
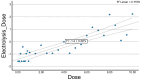
Background/Objectives: Percutaneous electrolysis is a physiotherapeutic technique based on the application of galvanic current to induce structural and biochemical changes in musculoskeletal tissues. Although widely used in tendinopathies, its application in muscle tissue, particularly regarding optimal dosage, remains poorly understood. This study aimed to evaluate the dose-dependent effects of galvanic current on cadaveric muscle tissue (medial gastrocnemius) using quantitative ultrasound analysis, and to identify objective biomarkers to guide dosage. Methods: An experimental model was employed, applying galvanic current at varying intensities (0-10.0 mA) to 29 samples of cadaveric medial gastrocnemius. Quantitative ultrasound parameters were measured, including geometric and textural features. Correlation analyses and simple and multiple linear regressions were performed to assess the relationship between current intensity and ultrasound variables. Additionally, dose segmentation into three groups (low: 0-1.0 mA, medium: 1.0-4.0 mA, high: >4.0 mA) allowed for comparative statistical analysis using Kruskal-Wallis and post hoc Mann-Whitney U tests. Results: Significant dose-response relationships were observed in key ultrasound parameters, including A_Number, A_Area, A_Perimeter, and A_Contrast (p < 0.001). Regression analysis revealed that a combination of A_Area, A_Number, and A_Perimeter accounted for 66.7% of the variance in applied dose (R2 = 0.667, p < 0.001), leading to the creation of the predictive variable Muscle_Electrolysis_Dose. Comparative analysis confirmed significant differences between low-, medium-, and high-dose groups, particularly between lower and higher doses. Conclusions: Quantitative ultrasound effectively detects structural changes in muscle tissue following percutaneous electrolysis. The results support the development of objective, image-based criteria for optimizing galvanic current dosage, enhancing the precision and personalization of treatment.
Keywords: dosage; galvanic current; muscle; percutaneous electrolysis; quantitative ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abat F., Valles S.L., Gelber P.E., Polidori F., Stitik T.P., García-Herreros S., Monllau J.C., Sanchez-Ibánez J.M. [Molecular Repair Mechanisms Using the Intratissue Percutaneous Electrolysis Technique in Patellar Tendonitis] Rev. Esp. Cir. Ortop. Traumatol. 2014;58:201–205. doi: 10.1016/j.recote.2014.05.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez-Sanz J., Rodríguez-Rodríguez S., López-de-Celis C., Malo-Urriés M., Pérez-Amodio S., Pérez-Antoñanzas R., Borrella-Andrés S., Albarova-Corral I., Mateos-Timoneda M.Á. Biological and Cellular Effects of Percutaneous Electrolysis: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines. 2024;12:2818. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122818. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abat F., Gelber P.E., Polidori F., Monllau J.C., Sanchez-Ibañez J.M. Clinical Results after Ultrasound-Guided Intratissue Percutaneous Electrolysis (EPI®) and Eccentric Exercise in the Treatment of Patellar Tendinopathy. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015;23:1046–1052. doi: 10.1007/s00167-014-2855-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Góngora-Rodríguez J., Rosety-Rodríguez M.Á., Rodríguez-Almagro D., Martín-Valero R., Góngora-Rodríguez P., Rodríguez-Huguet M. Structural and Functional Changes in Supraspinatus Tendinopathy through Percutaneous Electrolysis, Percutaneous Peripheral Nerve Stimulation and Eccentric Exercise Combined Therapy: A Single-Blinded Randomized Clinical Trial. Biomedicines. 2024;12:771. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040771. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arias-Buriá J.L., Truyols-Domínguez S., Valero-Alcaide R., Salom-Moreno J., Atín-Arratibel M.A., Fernández-De-Las-Penãs C. Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Electrolysis and Eccentric Exercises for Subacromial Pain Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2015;2015:315219. doi: 10.1155/2015/315219. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

