Time-to-Event Modeling for Survival Prediction of Osimertinib as the First- and Second-Line Therapy
- PMID: 40565824
- PMCID: PMC12194035
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14124077
Time-to-Event Modeling for Survival Prediction of Osimertinib as the First- and Second-Line Therapy
Abstract
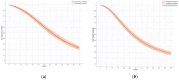
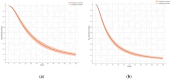
Objectives: To predict the survival rates of Osimertinib as first- and second-line therapy using time-to-event models based on literature data. Methods: Kaplan-Meier curves from randomized clinical trials were extracted after a systematic search of PubMed and Cochrane Library from their inception to 10 May 2023. Randomized clinical trials of Osimertinib reporting both first- and second-line overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) in NSCLC patients with specific mutations, compared to earlier epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors and chemotherapy. Kaplan-Meier curves of OS and PFS were extracted from published articles. A two-column raw dataset (time, survival probability) was extracted, and time-to-event outcomes (time, event) were derived using a graphic reconstructive algorithm. Data analysis was conducted from 1 June 2023 to 31 January 2024. Primary outcomes included OS and PFS for time-to-event modeling of Osimertinib as first- and second-line therapy. Results: The Weibull model, incorporating race as a covariate, best fit the first-line OS data. The log-logistic model best fit first-line PFS and second-line OS/PFS data. Based on these models, the predicted median OS for first-line and second-line treatment were 36.35 months (95% CI, 33.53-39.30 months) and 27.46 months (95% CI, 25.30-29.99 months), respectively. The predicted median PFS were 18.11 months (95% CI, 16.37-19.90 months) and 10.35 months (95% CI, 9.31-11.44 months), respectively. The predicted 3- and 5-year survival rates with first-line Osimertinib were 51% and 23%, respectively. Subgroup analysis revealed longer estimated 3- and 5-year survival rates for non-Asian patients compared to Asian patients (60% vs. 49% and 29% vs. 21%, respectively). Conclusions: The predicted survival rates from the time-to-event modeling align with the original clinical trial results, and an ethnic difference in Osimertinib efficacy was observed.
Keywords: Osimertinib; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); time-to-event modeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(15):iii-ix, xi-162. doi: 10.3310/hta12150. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18462574
-
Front-line therapy for brain metastases and non-brain metastases in advanced epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: a network meta-analysis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2023 Nov 5;136(21):2551-2561. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002468. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023. PMID: 37160733 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Treatment options for progression or recurrence of glioblastoma: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 4;5(1):CD013579. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013579.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34559423 Free PMC article.
-
First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3:CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub3. PMID: 27223332 Updated.
References
-
- Zhou C., Wu Y., Chen G., Feng J., Liu X.-Q., Wang C., Zhang S., Wang J., Zhou S., Ren S. Final overall survival results from a randomised, phase III study of erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802) Ann. Oncol. 2015;26:1877–1883. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv276. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fukuoka M., Wu Y.-L., Thongprasert S., Sunpaweravong P., Leong S.-S., Sriuranpong V., Chao T.-Y., Nakagawa K., Chu D.-T., Saijo N. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS) J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:2866–2874. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.4235. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous