Necrotizing Pneumonia as a Complication of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults at a Tertiary Institution
- PMID: 40565832
- PMCID: PMC12193808
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14124086
Necrotizing Pneumonia as a Complication of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults at a Tertiary Institution
Abstract
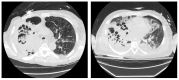
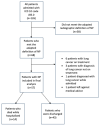
Background/Objectives: Necrotizing pneumonia (NP) is an uncommon, severe complication of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) associated with increased hospital length of stay and high morbidity and mortality. Although this entity was described several decades ago, there is no consensus on radiological criteria for diagnosis, optimal antibiotic duration, or data on clinical outcomes in adults. Given the paucity of data on this entity, a retrospective cohort study was conducted at our institution to evaluate factors associated with all-cause mortality, hospital length of stay, and duration of antibiotics. Methods: An IRB-approved retrospective cohort analysis was conducted through electronic health record review at a tertiary academic center at the University of Florida-Jacksonville. The electronic health record was queried for a list of all hospitalizations from 1 January 2016 to 31 December 2023 with an International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision diagnosis code of J85.0 (gangrene and necrosis of the lung). The primary outcome was all-cause mortality, and secondary outcomes were hospital length of stay and duration of antibiotics. Results: A total of 57 patients met the definition of necrotizing pneumonia and were included in our study. Fourteen (24.6%) patients died while hospitalized. The mean length of hospital stay was 26.6 days, and the median duration of antibiotics was 28 days. The only statistically significant predictor in the model of all-cause mortality was the requirement of mechanical ventilation, with mortality being 27 times more likely in patients requiring mechanical ventilation (OR 27.6 (95% CI (2.6924, 671.9648)); p = 0.011). Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the largest cohort of adult patients with NP in the literature. We found that mortality was 24.6%, with the requirement of mechanical ventilation associated with 27 times higher risk of mortality on multivariable logistic regression analysis.
Keywords: community-acquired pneumonia; mechanical ventilation; necrotizing pneumonia; pulmonary gangrene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous