Impact of Ectopic Pregnancy on the Outcomes of the Subsequent Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40565859
- PMCID: PMC12194004
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14124112
Impact of Ectopic Pregnancy on the Outcomes of the Subsequent Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
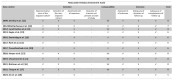
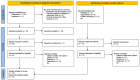
Background/Objectives: Although ectopic pregnancy has been extensively studied in terms of epidemiology, associated risk factors, diagnostic approaches, and treatment modalities, the data regarding its impact on the development of adverse outcomes in subsequent pregnancy remain scarce and conflicting. We aim to evaluate the adverse perinatal outcomes of women with a history of ectopic pregnancy Methods: We used the Medline (1966-2024), Scopus (2004-2024), Clinicaltrials.gov (2008-2024), EMBASE (1980-2024), Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials CENTRAL (1999-2024), and Google Scholar (2004-2024) databases in our primary search. All studies that evaluated the impact of prior of ectopic pregnancy on the perinatal outcomes of the subsequent pregnancy and reported rates of adverse perinatal outcomes were considered eligible for inclusion. Twelve peer-reviewed papers were considered for inclusion in our study. We enrolled a total of 2,162,731 women. Of those, 23,823 (1.1%) had a history of prior ectopic pregnancy. A total of 4 out of 12 studies provided the necessary data to be included in the metanalysis. Results: Women with a history of treated ectopic pregnancy, either medically or surgically, demonstrated increased risk of developing placental abruption, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and preterm birth. History of ectopic pregnancy was also positively associated with low birth weight, subsequent ectopic pregnancy, and increased risk of a subsequent emergency cesarean section. Conclusions: The meta-analysis reveals evidence that ectopic pregnancy is positively associated with adverse perinatal outcomes in subsequent pregnancy. Our findings should be considered preliminary and serve as a basis for future research as the retrieved data are scarce and cannot be deemed sufficient.
Keywords: ectopic pregnancy; emergency cesarean section; gestational hypertension; low birth weight; methotrexate; placental abruption; preterm delivery; salpingectomy; salpingostomy; tubal pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



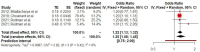
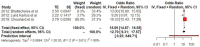

Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Multiple-micronutrient supplementation for women during pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 13;4(4):CD004905. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004905.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 14;3:CD004905. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004905.pub6. PMID: 28407219 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Treating periodontal disease for preventing adverse birth outcomes in pregnant women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 12;6(6):CD005297. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005297.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28605006 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Different intensities of glycaemic control for women with gestational diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 10;10(10):CD011624. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011624.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37815094 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

