Improved Cholesteatoma Removal with CADISS: A Quantitative Ultrastructural Comparison Using VP-SEM
- PMID: 40565938
- PMCID: PMC12194228
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14124192
Improved Cholesteatoma Removal with CADISS: A Quantitative Ultrastructural Comparison Using VP-SEM
Abstract
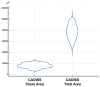
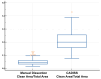
Background: Cholesteatoma is a destructive middle ear pathology requiring precise surgical removal to prevent recurrence and preserve auditory function. The chemically assisted dissection (CADISS) system (AuXin Surgery, Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium), based on Mesna (5%), was introduced to enhance tissue separation and minimize residual disease. Objective: This study aimed to compare the cleaning efficiency of CADISS-assisted dissection versus the conventional manual dissection of cholesteatoma from incus bone surfaces using quantitative ultrastructural analysis. Methods: This retrospective study evaluated 67 human incus samples collected during cholesteatoma surgery-35 treated with manual dissection and 32 with CADISS. Samples were imaged using variable pressure scanning electron microscopy (VP-SEM) in hydrated conditions. Clean area/total area ratios were calculated and analyzed statistically using non-parametric tests. Postoperative MRI follow-up at 1 month was conducted to assess residual disease. Results: CADISS-assisted samples demonstrated significantly higher clean area/total area ratios (mean: 0.2095 vs. 0.0478, p < 0.0001). Qualitative imaging showed fewer residuals > 1 mm in the CADISS group (9% vs. 77%). MRI follow-up revealed a lower recurrence rate in the CADISS group (3.1%) compared to manual dissection (11.4%). Conclusions: CADISS-assisted dissection provides superior cholesteatoma debris removal compared to manual methods, as evidenced by VP-SEM imaging and clinical follow-up. This technique may improve surgical outcomes and reduce recurrence risk in middle ear surgery.
Keywords: VP-SEM imaging; chemical-assisted dissection; cholesteatoma surgery; residual disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Guided tissue regeneration for periodontal infra-bony defects.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Apr 19;(2):CD001724. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001724.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 May 29;5:CD001724. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001724.pub3. PMID: 16625546 Updated.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Enamel matrix derivative (Emdogain) for periodontal tissue regeneration in intrabony defects. A Cochrane systematic review.Eur J Oral Implantol. 2009 Winter;2(4):247-66. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2009. PMID: 20467602
-
Rehabilitation for ankle fractures in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11:CD005595. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005595.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Sep 23;9:CD005595. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005595.pub4. PMID: 23152232 Updated.
-
Surgery for trigger finger.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 20;2(2):CD009860. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009860.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29460276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yung M., Tono T., Olszewska E., Yamamoto Y., Sudhoff H., Sakagami M., Mulder J., Kojima H., İncesulu A., Trabalzini F., et al. EAONO/JOS joint consensus statements on the definitions, classification and staging of middle ear cholesteatoma. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2017;13:1–8. doi: 10.5152/iao.2017.3363. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

