Associations Between Glycemic Control, Self-Reported Gingival Bleeding and Lifestyle Factors in Hospitalized Diabetic Patients
- PMID: 40565947
- PMCID: PMC12194272
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14124201
Associations Between Glycemic Control, Self-Reported Gingival Bleeding and Lifestyle Factors in Hospitalized Diabetic Patients
Abstract
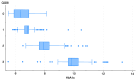
Background/Objectives: Diabetes mellitus is associated with significant health complications, including challenges in periodontal health. Gingival inflammation is especially common among diabetic patients and can significantly impact overall diabetes management. This study aims to investigate the correlation between glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, an established marker of glycemic control, and gingival inflammation using the Quantitative Gingival Bleeding Index (QGBI) among hospitalized diabetic patients, thereby placing the question within a broader clinical context. Methods: The study enrolled 671 hospitalized patients with diabetes complications at "Mother Theresa University Hospital" in Tirana, AL, USA. Glycemic control was assessed through glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, and gingival health was evaluated using the Quantitative Gingival Bleeding Index (QGBI). Behavioral variables were also documented, including smoking habits and routine oral care practices. Spearman's correlation coefficient (rs) was applied to determine the relationship between HbA1c levels and QGBI scores. Results: Our findings revealed a strong positive correlation between glycemic control (HbA1c) and gingival inflammation (QGBI) among the participants (Spearman's coefficient rs = 0.868, p < 0.001). Additionally, significant positive associations were observed between behavioral factors, such as smoking habits and regular oral care practices, further underscoring their role in periodontal health in diabetic patients. Conclusions: The study highlights a significant positive relationship between poor glycemic control and increased gingival inflammation, emphasizing the importance of periodontal health in the comprehensive management of diabetes mellitus. Our results support integrating periodontal evaluation and management into standard diabetes care, which could improve patient outcomes and overall well-being.
Keywords: HbA1c levels; Quantitative Gingival Bleeding Index; dental care; diabetes mellitus; gingival health; hospitalized patients; oral health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of periodontitis for glycaemic control in people with diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 14;4(4):CD004714. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004714.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35420698 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorhexidine mouthrinse as an adjunctive treatment for gingival health.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 31;3(3):CD008676. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008676.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28362061 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile phone messaging for facilitating self-management of long-term illnesses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD007459. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007459.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235644 Free PMC article.
-
Quality improvement strategies for diabetes care: Effects on outcomes for adults living with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 31;5(5):CD014513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014513. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37254718 Free PMC article.
-
Multidisciplinary management of diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Jul;14(7):169-207. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003011. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532796
References
-
- Magliano D.J., Boyko E.J., IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition Scientific Committee . IDF DIABETES ATLAS [Internet] 10th ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

