Recovery and Protective Effect of Direct Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation in the Treatment of Acute and Subacute Fibular Tunnel Syndrome
- PMID: 40565993
- PMCID: PMC12194285
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14124247
Recovery and Protective Effect of Direct Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation in the Treatment of Acute and Subacute Fibular Tunnel Syndrome
Abstract
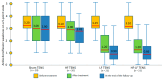
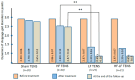
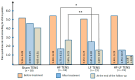
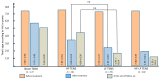
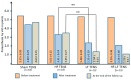
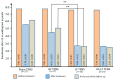
Background: Previous studies have indicated that transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is highly effective in improving the treatment of neuropathy and achieving maximum recovery in the shortest time. However, its effectiveness in the early stages of the disease has not been studied, and no comparative analysis has been conducted between different modalities of TENS. Materials and Methods: This study included 82 patients with acute and subacute fibular tunnel (FT) syndrome lasting no more than 15 days. Patients were randomized into the following four groups depending on the modality of TENS used: sham TENS (20 patients), HF TENS (20 patients), LF TENS (21 patients), and a combined HF/LF TENS group (21 patients). Before treatment, immediately after treatment, and 3 months after the end of treatment patients were examined to determine the severity of hypoesthesia, motor deficit, and gait disturbance. Results: The reduction in hypoesthesia averaged after HF TENS, LF TENS, and sham TENS was 50.7% (p ≤ 0.01), 37.8 (p ≤ 0.01), and 11.4% (p > 0.05), respectively. The regression of motor deficit and gate disorders reached 61% after LF TENS (p ≤ 0.01), 6% after HF TENS (p > 0.05), and 6% (p > 0.05) after sham TENS. The combination of HF and LF TENS resulted in a 54.8% (p ≤ 0.01) reduction in hypoesthesia and 61.3% (p ≤ 0.01) regression of motor deficit, with a superior 30% (p ≤ 0.05) improvement in quality of life compared to separate use of HF and LF TENS. Conclusions: Early use of TENS in the treatment of FT syndrome turned out to be highly effective compared to sham TENS in reducing hypoesthesia, motor deficit, and gait disturbance. The analgesic effect and sensory recovery were higher after HF TENS. Motor and gait disturbances were reduced only after LF TENS, with evidence of prolonged regenerative and protective effect for at least 3 months after the end of treatment. The combination of HF TENS and LF TENS increases the therapeutic range of TENS with the achievement of the maximum positive effect of HF TENS and LF TENS after treatment and during the long-term period, which leads to a more pronounced improvement in the quality of life of patients with this pathology.
Keywords: TENS; common peroneal nerve; fibular tunnel syndrome; neuropathy; recovery; transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Poppler L.H., Groves A.P., Sacks G., Bansal A., Davidge K.M., Sledge J.A., Tymkew H., Yan Y., Hasak J.M., Potter P., et al. Subclinical Peroneal Neuropathy: A Common, Unrecognized, and Preventable Finding Associated with a Recent History of Falling in Hospitalized Patients. Ann. Fam. Med. 2016;14:526–533. doi: 10.1370/afm.1973. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

