The 4Rs Framework of Sports Nutrition: An Update with Recommendations to Evaluate Allostatic Load in Athletes
- PMID: 40566521
- PMCID: PMC12194569
- DOI: 10.3390/life15060867
The 4Rs Framework of Sports Nutrition: An Update with Recommendations to Evaluate Allostatic Load in Athletes
Abstract
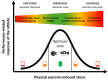
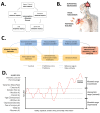
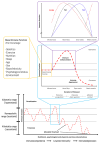
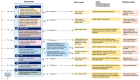
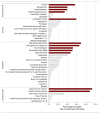
The 4Rs of sports nutrition were proposed in recent years as an evidence-based framework to optimize post-exercise recovery within the context of allostasis. Under this paradigm, it is important to consider that each R represents a factor with a tremendous influence on the allostatic response and improves individual components of the allostatic load (AL), which will positively impact the exercise-induced adaptations and the athlete's recovery. The 4Rs correspond to the following. (i) Rehydration-This is necessary to guarantee the post-exercise consumption of at least 150% of the body mass lost during the exercise accompanied by sodium (if faster replacement is required). (ii) Refuel-Carbohydrate intake (~1.2 g/kg body mass per hour for up to 4 h post-exercise) is essential not only in restoring glycogen reserves but also in supporting the energy needs of the immune system and facilitating tissue repair. Despite changes in substrate utilization, a ketogenic diet generally has neutral or negative effects on athletic performance compared to carbohydrate-rich diets. (iii) Repair-The ingestion of high-quality protein stimulates post-exercise net muscle protein anabolism and might contribute to faster tissue growth and repair. The use of certain supplements, such as creatine monohydrate, might help to enhance recovery, while tart cherry, omega-3 fatty acids, and dietary nitrate (e.g., Beta vulgaris, Amaranthus L.), as well as other herbal extracts containing flavonoid-rich polyphenols, deserve further clinical research. (iv) Recuperate-Pre-sleep nutrition (casein- or protein-rich meal with slow digestion rate) has a restorative effect, facilitating the recovery of the musculoskeletal, endocrine, immune, and nervous systems. In this article, we update the 4Rs framework, delve deeper into the allostasis paradigm, and offer theoretical foundations and practical recommendations (the 4Rs app) for the assessment of AL in athletes. We cautiously propose an AL index (ALindex) for physique competitors and elite athletes to evaluate the cumulative physiological stress induced by exercise and, thereby, to adjust exercise and nutrition interventions.
Keywords: allostasis; biomarkers; cacostasis; physiological adaptation; sports nutritional sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
D.A.B. serves as the scientific and managing director of KreaFood, an R&D&I Project; has served as the science product manager for the MTX Corporation® in Europe; has acted as a scientific consultant for MET-Rx® and Healthy Sports in Colombia; has conducted academic-sponsored research on nutritional supplements; and receives honoraria for speaking about sports nutrition at international conferences and private courses. R.B.K. has conducted industry-sponsored research on dietary supplements; received financial support for presentations about dietary supplements at industry-sponsored scientific conferences; and has served as an expert witness on cases related to exercise, nutrition, and dietary supplementation. B.I.C. has received grants and contracts to conduct research on dietary supplements; has served as a paid consultant for industry; has received honoraria for speaking at conferences and writing lay articles about sports nutrition ingredients and topics; and has served as an expert witness on cases involving dietary supplements. G.E. serves on the Scientific Advisory Board and as the lead Physique and Bodybuilding Program subject matter expert for the National Academy of Sports Medicine; he has also served as a paid scientific consultant for various dietary supplement companies. J.R.S. has conducted industry-sponsored research on sports nutrition over the past 25 years. Further, J.R.S. has also received financial support for presenting on the science of various nutraceuticals, at industry-sponsored scientific conferences. M.G. has received grants and contracts to conduct research on sport nutrition products and dietary supplements; has served as a paid consultant for industry; and has received honoraria for speaking at conferences and writing lay articles about sports nutrition ingredients and topics. Finally, R.B.K. serves as Chair of the “Creatine for Health” scientific advisory board sponsored by Creapure® and Creavitalis®—Alzchem Group AG, while D.A.B., B.I.C., and J.R.S. serve as members of this board. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Effects of dietary supplements on athletic performance in elite soccer players: a systematic review.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023 Dec;20(1):2236060. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2023.2236060. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37462346 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Strategies in the Rehabilitation of Musculoskeletal Injuries in Athletes: A Systematic Integrative Review.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 5;15(4):819. doi: 10.3390/nu15040819. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36839176 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for promoting habitual exercise in people living with and beyond cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 19;9(9):CD010192. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010192.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30229557 Free PMC article.
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonilla D.A., Perez-Idarraga A., Odriozola-Martinez A., Kreider R.B. The 4R’s Framework of Nutritional Strategies for Post-Exercise Recovery: A Review with Emphasis on New Generation of Carbohydrates. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020;18:103. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18010103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bonilla D.A., Cardozo L.A., Velez-Gutierrez J.M., Arevalo-Rodriguez A., Vargas-Molina S., Stout J.R., Kreider R.B., Petro J.L. Exercise Selection and Common Injuries in Fitness Centers: A Systematic Integrative Review and Practical Recommendations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022;19:12710. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912710. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rowlands D.S., Kopetschny B.H., Badenhorst C.E. The Hydrating Effects of Hypertonic, Isotonic and Hypotonic Sports Drinks and Waters on Central Hydration During Continuous Exercise: A Systematic Meta-Analysis and Perspective. Sports Med. 2022;52:349–375. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01558-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

