Trophoblast Extracellular Vesicles as Modulators of Keratinocyte Stress Response and Senescence
- PMID: 40566570
- PMCID: PMC12194262
- DOI: 10.3390/life15060918
Trophoblast Extracellular Vesicles as Modulators of Keratinocyte Stress Response and Senescence
Abstract
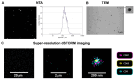
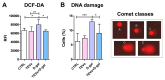
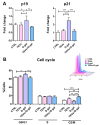
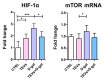
Keratinocyte stress, caused by various intrinsic and extrinsic factors, contributes to the overall aging process. D-galactose-induced metabolic/oxidative stress is a commonly used in vitro model for studying premature aging. Due to their rich composition of bioactive molecules that influence critical pathways in cellular aging and rejuvenation, placental derivatives have a well-established history in anti-aging skincare and therapy. However, trophoblast-derived extracellular vesicle (TEV) effects on D-galactose-induced premature aging in keratinocytes have not been investigated yet. TEV pretreatment for 24 h enhanced cellular resilience against D-galactose-induced stress, judging by the downregulated expression of senescence- and stress-associated markers (p19 and p21, HIF-1α, mTOR), and reduced production of reactive oxygen species and DNA damage. Additionally, TEV pretreatment enhanced keratinocyte proliferation and integrin-β1 subunit expression upon D-galactose exposure, most likely contributing to more efficient wound closure. In conclusion, this study underscores the potential of TEVs to modify expression of stress- and senescence-related proteins in keratinocytes and improve their wound healing properties. Their regenerative and protective characteristics position TEVs as promising candidates for developing innovative procedures to address skin conditions related to premature aging.
Keywords: aging; placenta; regenerative medicine; skin; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

