A Possible Involvement of Sialidase in the Cell Response of the Antarctic Fungus Penicillium griseofulvum P29 to Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 40566577
- PMCID: PMC12194652
- DOI: 10.3390/life15060926
A Possible Involvement of Sialidase in the Cell Response of the Antarctic Fungus Penicillium griseofulvum P29 to Oxidative Stress
Abstract
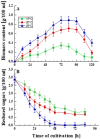
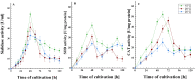
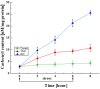
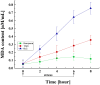
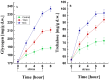
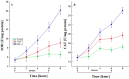
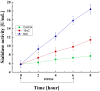
Sialidases/neuraminidases remove terminal sialic acid residues from glycoproteins, glycolipids, and oligosaccharides. Our previous research has revealed the distribution of sialidase in non-clinical fungal isolates from different ecological niches, including Antarctica. Fungi adapted to extremely low temperatures possess defense mechanisms necessary for their survival such as the response against oxidative stress. The relationship between oxidative stress and sialidase synthesis has been studied extremely sparsely. The aim of the present study was to investigate the involvement of sialidase in the cell response of the Antarctic strain P. griseofulvum P29 against oxidative stress induced by long- and short-term exposure to low temperatures. The changes in growth temperatures for 120 h (long-term stress) affected biomass accumulation, glucose consumption, sialidase synthesis, and the activity of the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT). The short-term temperature downshift (6 h) caused oxidative stress, evidenced by changes in the levels of biomarkers, including lipid peroxidation, oxidatively damaged proteins, and the accumulation of reserve carbohydrates. Simultaneously, a sharp increase in SOD and CAT activity was found, which coincided with a significant increase in sialidase activity. This study marks the first demonstration of increased sialidase activity in filamentous fungi isolated from extreme cold environments as a response to oxidative stress.
Keywords: Antarctica; antioxidant enzymes; cold stress; fungi; oxidative stress biomarkers; sialidase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

